diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3220_odd_and_even_transactions/script.sql b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3220_odd_and_even_transactions/script.sql
index 33c0eda87..17b7930c5 100644
--- a/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3220_odd_and_even_transactions/script.sql
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3220_odd_and_even_transactions/script.sql
@@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
# Write your MySQL query statement below
-# #Medium #2024_07_18_Time_272_ms_(100.00%)_Space_0B_(100.00%)
+# #Medium #Database #2024_07_23_Time_248_ms_(85.85%)_Space_0B_(100.00%)
select transaction_date,
sum(case when amount%2<>0 then amount else 0 end) as odd_sum,
sum(case when amount%2=0 then amount else 0 end) as even_sum from transactions
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3222_find_the_winning_player_in_coin_game/Solution.kt b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3222_find_the_winning_player_in_coin_game/Solution.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..9fa216d28
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3222_find_the_winning_player_in_coin_game/Solution.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3222_find_the_winning_player_in_coin_game
+
+// #Easy #Math #Simulation #Game_Theory #2024_07_23_Time_140_ms_(86.44%)_Space_34.3_MB_(77.97%)
+
+class Solution {
+ fun losingPlayer(x: Int, y: Int): String {
+ var x = x
+ var y = y
+ var w = false
+ while (x > 0 && y >= 4) {
+ x--
+ y -= 4
+ w = !w
+ }
+ return if (w) "Alice" else "Bob"
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3222_find_the_winning_player_in_coin_game/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3222_find_the_winning_player_in_coin_game/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..649d5f0d0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3222_find_the_winning_player_in_coin_game/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,38 @@
+3222\. Find the Winning Player in Coin Game
+
+Easy
+
+You are given two **positive** integers `x` and `y`, denoting the number of coins with values 75 and 10 _respectively_.
+
+Alice and Bob are playing a game. Each turn, starting with **Alice**, the player must pick up coins with a **total** value 115. If the player is unable to do so, they **lose** the game.
+
+Return the _name_ of the player who wins the game if both players play **optimally**.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** x = 2, y = 7
+
+**Output:** "Alice"
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+The game ends in a single turn:
+
+* Alice picks 1 coin with a value of 75 and 4 coins with a value of 10.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** x = 4, y = 11
+
+**Output:** "Bob"
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+The game ends in 2 turns:
+
+* Alice picks 1 coin with a value of 75 and 4 coins with a value of 10.
+* Bob picks 1 coin with a value of 75 and 4 coins with a value of 10.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= x, y <= 100`
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3223_minimum_length_of_string_after_operations/Solution.kt b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3223_minimum_length_of_string_after_operations/Solution.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..1060a0871
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3223_minimum_length_of_string_after_operations/Solution.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,26 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3223_minimum_length_of_string_after_operations
+
+// #Medium #String #Hash_Table #Counting #2024_07_23_Time_316_ms_(60.00%)_Space_48.4_MB_(82.22%)
+
+class Solution {
+ fun minimumLength(s: String): Int {
+ val freq = IntArray(26)
+ for (i in 0..25) {
+ freq[i] = 0
+ }
+ for (i in 0 until s.length) {
+ freq[s[i].code - 'a'.code]++
+ }
+ var c = 0
+ for (i in freq) {
+ if (i != 0) {
+ c += if (i % 2 == 0) {
+ 2
+ } else {
+ 1
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return c
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3223_minimum_length_of_string_after_operations/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3223_minimum_length_of_string_after_operations/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..a53d43938
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3223_minimum_length_of_string_after_operations/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,39 @@
+3223\. Minimum Length of String After Operations
+
+Medium
+
+You are given a string `s`.
+
+You can perform the following process on `s` **any** number of times:
+
+* Choose an index `i` in the string such that there is **at least** one character to the left of index `i` that is equal to `s[i]`, and **at least** one character to the right that is also equal to `s[i]`.
+* Delete the **closest** character to the **left** of index `i` that is equal to `s[i]`.
+* Delete the **closest** character to the **right** of index `i` that is equal to `s[i]`.
+
+Return the **minimum** length of the final string `s` that you can achieve.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** s = "abaacbcbb"
+
+**Output:** 5
+
+**Explanation:**
+ We do the following operations:
+
+* Choose index 2, then remove the characters at indices 0 and 3. The resulting string is `s = "bacbcbb"`.
+* Choose index 3, then remove the characters at indices 0 and 5. The resulting string is `s = "acbcb"`.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** s = "aa"
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:**
+ We cannot perform any operations, so we return the length of the original string.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= s.length <= 2 * 105
+* `s` consists only of lowercase English letters.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3224_minimum_array_changes_to_make_differences_equal/Solution.kt b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3224_minimum_array_changes_to_make_differences_equal/Solution.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..b29f7f1b7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3224_minimum_array_changes_to_make_differences_equal/Solution.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3224_minimum_array_changes_to_make_differences_equal
+
+// #Medium #Array #Hash_Table #Prefix_Sum #2024_07_23_Time_665_ms_(84.62%)_Space_69.3_MB_(53.85%)
+
+import kotlin.math.max
+import kotlin.math.min
+
+class Solution {
+ fun minChanges(nums: IntArray, k: Int): Int {
+ val cm = IntArray(k + 2)
+ for (i in 0 until nums.size / 2) {
+ val a = min(nums[i], nums[nums.size - 1 - i])
+ val b = max(nums[i], nums[nums.size - 1 - i])
+ val d = b - a
+ if (d > 0) {
+ cm[0]++
+ cm[d]--
+ cm[d + 1]++
+ val max = (max(a, (k - b)) + d)
+ cm[max + 1]++
+ } else {
+ cm[1]++
+ val max = max(a, (k - a))
+ cm[max + 1]++
+ }
+ }
+ var sum = cm[0]
+ var res = cm[0]
+ for (i in 1..k) {
+ sum += cm[i]
+ res = min(res, sum)
+ }
+ return res
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3224_minimum_array_changes_to_make_differences_equal/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3224_minimum_array_changes_to_make_differences_equal/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..b3b22283e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3224_minimum_array_changes_to_make_differences_equal/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,47 @@
+3224\. Minimum Array Changes to Make Differences Equal
+
+Medium
+
+You are given an integer array `nums` of size `n` where `n` is **even**, and an integer `k`.
+
+You can perform some changes on the array, where in one change you can replace **any** element in the array with **any** integer in the range from `0` to `k`.
+
+You need to perform some changes (possibly none) such that the final array satisfies the following condition:
+
+* There exists an integer `X` such that `abs(a[i] - a[n - i - 1]) = X` for all `(0 <= i < n)`.
+
+Return the **minimum** number of changes required to satisfy the above condition.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,0,1,2,4,3], k = 4
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:**
+ We can perform the following changes:
+
+* Replace `nums[1]` by 2. The resulting array is nums = [1,**2**,1,2,4,3].
+* Replace `nums[3]` by 3. The resulting array is nums = [1,2,1,**3**,4,3].
+
+The integer `X` will be 2.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [0,1,2,3,3,6,5,4], k = 6
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:**
+ We can perform the following operations:
+
+* Replace `nums[3]` by 0. The resulting array is nums = [0,1,2,**0**,3,6,5,4].
+* Replace `nums[4]` by 4. The resulting array is nums = [0,1,2,0,**4**,6,5,4].
+
+The integer `X` will be 4.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 2 <= n == nums.length <= 105
+* `n` is even.
+* 0 <= nums[i] <= k <= 105
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3225_maximum_score_from_grid_operations/Solution.kt b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3225_maximum_score_from_grid_operations/Solution.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..486879ed3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3225_maximum_score_from_grid_operations/Solution.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,61 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3225_maximum_score_from_grid_operations
+
+// #Hard #Array #Dynamic_Programming #Matrix #Prefix_Sum
+// #2024_07_23_Time_371_ms_(100.00%)_Space_49.9_MB_(100.00%)
+
+import kotlin.math.max
+
+class Solution {
+ fun maximumScore(grid: Array): Long {
+ val n = grid.size
+ var dp1 = LongArray(n)
+ var dp2 = LongArray(n + 1)
+ var dp3 = LongArray(n + 1)
+ var dp12 = LongArray(n)
+ var dp22 = LongArray(n + 1)
+ var dp32 = LongArray(n + 1)
+ var res: Long = 0
+ for (i in 0 until n) {
+ var sum: Long = 0
+ var pre: Long = 0
+ for (ints in grid) {
+ sum += ints[i].toLong()
+ }
+ for (j in n - 1 downTo 0) {
+ var s2 = sum
+ dp12[j] = s2 + dp3[n]
+ for (k in 0..j) {
+ s2 -= grid[k][i].toLong()
+ var v = max((dp1[k] + s2), (dp3[j] + s2))
+ v = max(v, (pre + s2))
+ dp12[j] = max(dp12[j], v)
+ if (k == j) {
+ dp32[j] = v
+ dp22[j] = dp32[j]
+ res = max(res, v)
+ }
+ }
+ if (i > 0) {
+ pre = max((pre + grid[j][i]), (dp2[j] + grid[j][i]))
+ }
+ sum -= grid[j][i].toLong()
+ }
+ dp32[n] = pre
+ dp22[n] = dp32[n]
+ res = max(res, pre)
+ for (j in 1..n) {
+ dp32[j] = max(dp32[j], dp32[j - 1])
+ }
+ var tem = dp1
+ dp1 = dp12
+ dp12 = tem
+ tem = dp2
+ dp2 = dp22
+ dp22 = tem
+ tem = dp3
+ dp3 = dp32
+ dp32 = tem
+ }
+ return res
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3225_maximum_score_from_grid_operations/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3225_maximum_score_from_grid_operations/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..90081c6fc
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3225_maximum_score_from_grid_operations/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,39 @@
+3225\. Maximum Score From Grid Operations
+
+Hard
+
+You are given a 2D matrix `grid` of size `n x n`. Initially, all cells of the grid are colored white. In one operation, you can select any cell of indices `(i, j)`, and color black all the cells of the jth column starting from the top row down to the ith row.
+
+The grid score is the sum of all `grid[i][j]` such that cell `(i, j)` is white and it has a horizontally adjacent black cell.
+
+Return the **maximum** score that can be achieved after some number of operations.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
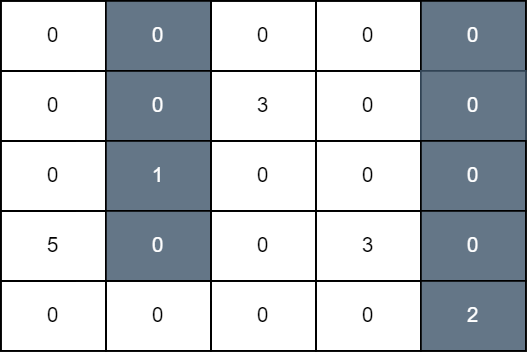
+**Input:** grid = [[0,0,0,0,0],[0,0,3,0,0],[0,1,0,0,0],[5,0,0,3,0],[0,0,0,0,2]]
+
+**Output:** 11
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+
+
+In the first operation, we color all cells in column 1 down to row 3, and in the second operation, we color all cells in column 4 down to the last row. The score of the resulting grid is `grid[3][0] + grid[1][2] + grid[3][3]` which is equal to 11.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
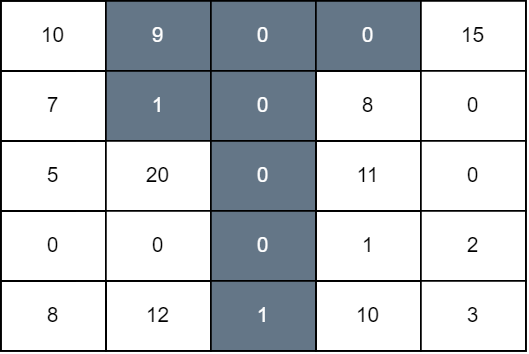
+**Input:** grid = [[10,9,0,0,15],[7,1,0,8,0],[5,20,0,11,0],[0,0,0,1,2],[8,12,1,10,3]]
+
+**Output:** 94
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+
+
+We perform operations on 1, 2, and 3 down to rows 1, 4, and 0, respectively. The score of the resulting grid is `grid[0][0] + grid[1][0] + grid[2][1] + grid[4][1] + grid[1][3] + grid[2][3] + grid[3][3] + grid[4][3] + grid[0][4]` which is equal to 94.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= n == grid.length <= 100`
+* `n == grid[i].length`
+* 0 <= grid[i][j] <= 109
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3226_number_of_bit_changes_to_make_two_integers_equal/Solution.kt b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3226_number_of_bit_changes_to_make_two_integers_equal/Solution.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..0fb07ea44
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3226_number_of_bit_changes_to_make_two_integers_equal/Solution.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,24 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3226_number_of_bit_changes_to_make_two_integers_equal
+
+// #Easy #Bit_Manipulation #2024_07_23_Time_136_ms_(61.90%)_Space_33.2_MB_(90.48%)
+
+class Solution {
+ fun minChanges(n: Int, k: Int): Int {
+ var n = n
+ var k = k
+ if ((n or k) != n) {
+ return -1
+ }
+ var cnt = 0
+ while (n > 0 || k > 0) {
+ val bitN = n and 1
+ val bitK = k and 1
+ if (bitN == 1 && bitK == 0) {
+ cnt++
+ }
+ n = n shr 1
+ k = k shr 1
+ }
+ return cnt
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3226_number_of_bit_changes_to_make_two_integers_equal/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3226_number_of_bit_changes_to_make_two_integers_equal/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..e03ae0e81
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3226_number_of_bit_changes_to_make_two_integers_equal/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,41 @@
+3226\. Number of Bit Changes to Make Two Integers Equal
+
+Easy
+
+You are given two positive integers `n` and `k`.
+
+You can choose **any** bit in the **binary representation** of `n` that is equal to 1 and change it to 0.
+
+Return the _number of changes_ needed to make `n` equal to `k`. If it is impossible, return -1.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** n = 13, k = 4
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:**
+ Initially, the binary representations of `n` and `k` are n = (1101)2 and k = (0100)2.
+ We can change the first and fourth bits of `n`. The resulting integer is n = (**0**10**0**)2 = k.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** n = 21, k = 21
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Explanation:**
+ `n` and `k` are already equal, so no changes are needed.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** n = 14, k = 13
+
+**Output:** \-1
+
+**Explanation:**
+ It is not possible to make `n` equal to `k`.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= n, k <= 106
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3227_vowels_game_in_a_string/Solution.kt b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3227_vowels_game_in_a_string/Solution.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..f6f0b90d2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3227_vowels_game_in_a_string/Solution.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,15 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3227_vowels_game_in_a_string
+
+// #Medium #String #Math #Game_Theory #Brainteaser
+// #2024_07_23_Time_234_ms_(90.32%)_Space_38.9_MB_(83.87%)
+
+class Solution {
+ fun doesAliceWin(s: String): Boolean {
+ for (element in s) {
+ if (element == 'a' || element == 'e' || element == 'i' || element == 'o' || element == 'u') {
+ return true
+ }
+ }
+ return false
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3227_vowels_game_in_a_string/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3227_vowels_game_in_a_string/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..770a35741
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3227_vowels_game_in_a_string/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,44 @@
+3227\. Vowels Game in a String
+
+Medium
+
+Alice and Bob are playing a game on a string.
+
+You are given a string `s`, Alice and Bob will take turns playing the following game where Alice starts **first**:
+
+* On Alice's turn, she has to remove any **non-empty** substring from `s` that contains an **odd** number of vowels.
+* On Bob's turn, he has to remove any **non-empty** substring from `s` that contains an **even** number of vowels.
+
+The first player who cannot make a move on their turn loses the game. We assume that both Alice and Bob play **optimally**.
+
+Return `true` if Alice wins the game, and `false` otherwise.
+
+The English vowels are: `a`, `e`, `i`, `o`, and `u`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** s = "leetcoder"
+
+**Output:** true
+
+**Explanation:**
+ Alice can win the game as follows:
+
+* Alice plays first, she can delete the underlined substring in s = "**leetco**der" which contains 3 vowels. The resulting string is `s = "der"`.
+* Bob plays second, he can delete the underlined substring in s = "**d**er" which contains 0 vowels. The resulting string is `s = "er"`.
+* Alice plays third, she can delete the whole string s = "**er**" which contains 1 vowel.
+* Bob plays fourth, since the string is empty, there is no valid play for Bob. So Alice wins the game.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** s = "bbcd"
+
+**Output:** false
+
+**Explanation:**
+ There is no valid play for Alice in her first turn, so Alice loses the game.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= s.length <= 105
+* `s` consists only of lowercase English letters.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3228_maximum_number_of_operations_to_move_ones_to_the_end/Solution.kt b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3228_maximum_number_of_operations_to_move_ones_to_the_end/Solution.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..74e061fc3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3228_maximum_number_of_operations_to_move_ones_to_the_end/Solution.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,19 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3228_maximum_number_of_operations_to_move_ones_to_the_end
+
+// #Medium #String #Greedy #Counting #2024_07_23_Time_232_ms_(44.00%)_Space_38_MB_(96.00%)
+
+class Solution {
+ fun maxOperations(s: String): Int {
+ val arr = s.toCharArray()
+ var result = 0
+ var ones = 0
+ val n = arr.size
+ for (i in 0 until n) {
+ ones += arr[i].code - '0'.code
+ if (i > 0 && arr[i] < arr[i - 1]) {
+ result += ones
+ }
+ }
+ return result
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3228_maximum_number_of_operations_to_move_ones_to_the_end/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3228_maximum_number_of_operations_to_move_ones_to_the_end/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..edd953a6f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3228_maximum_number_of_operations_to_move_ones_to_the_end/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,38 @@
+3228\. Maximum Number of Operations to Move Ones to the End
+
+Medium
+
+You are given a binary string `s`.
+
+You can perform the following operation on the string **any** number of times:
+
+* Choose **any** index `i` from the string where `i + 1 < s.length` such that `s[i] == '1'` and `s[i + 1] == '0'`.
+* Move the character `s[i]` to the **right** until it reaches the end of the string or another `'1'`. For example, for `s = "010010"`, if we choose `i = 1`, the resulting string will be s = "0**001**10".
+
+Return the **maximum** number of operations that you can perform.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** s = "1001101"
+
+**Output:** 4
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+We can perform the following operations:
+
+* Choose index `i = 0`. The resulting string is s = "**001**1101".
+* Choose index `i = 4`. The resulting string is s = "0011**01**1".
+* Choose index `i = 3`. The resulting string is s = "001**01**11".
+* Choose index `i = 2`. The resulting string is s = "00**01**111".
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** s = "00111"
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= s.length <= 105
+* `s[i]` is either `'0'` or `'1'`.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3229_minimum_operations_to_make_array_equal_to_target/Solution.kt b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3229_minimum_operations_to_make_array_equal_to_target/Solution.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..d4d597bcb
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3229_minimum_operations_to_make_array_equal_to_target/Solution.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3229_minimum_operations_to_make_array_equal_to_target
+
+// #Hard #Array #Dynamic_Programming #Greedy #Stack #Monotonic_Stack
+// #2024_07_23_Time_636_ms_(57.14%)_Space_71.7_MB_(28.57%)
+
+class Solution {
+ fun minimumOperations(nums: IntArray, target: IntArray): Long {
+ val n = nums.size
+ var incr: Long = 0
+ var decr: Long = 0
+ var ops: Long = 0
+ for (i in 0 until n) {
+ val diff = target[i] - nums[i]
+ if (diff > 0) {
+ if (incr < diff) {
+ ops += diff - incr
+ }
+ incr = diff.toLong()
+ decr = 0
+ } else if (diff < 0) {
+ if (decr < -diff) {
+ ops += -diff - decr
+ }
+ decr = -diff.toLong()
+ incr = 0
+ } else {
+ decr = 0
+ incr = decr
+ }
+ }
+ return ops
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3229_minimum_operations_to_make_array_equal_to_target/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3229_minimum_operations_to_make_array_equal_to_target/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..12dc0737e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3229_minimum_operations_to_make_array_equal_to_target/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,41 @@
+3229\. Minimum Operations to Make Array Equal to Target
+
+Hard
+
+You are given two positive integer arrays `nums` and `target`, of the same length.
+
+In a single operation, you can select any subarray of `nums` and increment or decrement each element within that subarray by 1.
+
+Return the **minimum** number of operations required to make `nums` equal to the array `target`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [3,5,1,2], target = [4,6,2,4]
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+We will perform the following operations to make `nums` equal to `target`:
+ \- Increment `nums[0..3]` by 1, `nums = [4,6,2,3]`.
+ \- Increment `nums[3..3]` by 1, `nums = [4,6,2,4]`.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,3,2], target = [2,1,4]
+
+**Output:** 5
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+We will perform the following operations to make `nums` equal to `target`:
+ \- Increment `nums[0..0]` by 1, `nums = [2,3,2]`.
+ \- Decrement `nums[1..1]` by 1, `nums = [2,2,2]`.
+ \- Decrement `nums[1..1]` by 1, `nums = [2,1,2]`.
+ \- Increment `nums[2..2]` by 1, `nums = [2,1,3]`.
+ \- Increment `nums[2..2]` by 1, `nums = [2,1,4]`.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= nums.length == target.length <= 105
+* 1 <= nums[i], target[i] <= 108
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/test/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3222_find_the_winning_player_in_coin_game/SolutionTest.kt b/src/test/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3222_find_the_winning_player_in_coin_game/SolutionTest.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..d6d99d2c3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3222_find_the_winning_player_in_coin_game/SolutionTest.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3222_find_the_winning_player_in_coin_game
+
+import org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo
+import org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
+
+internal class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ fun losingPlayer() {
+ assertThat(Solution().losingPlayer(2, 7), equalTo("Alice"))
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun losingPlayer2() {
+ assertThat(Solution().losingPlayer(4, 11), equalTo("Bob"))
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3223_minimum_length_of_string_after_operations/SolutionTest.kt b/src/test/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3223_minimum_length_of_string_after_operations/SolutionTest.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..a8745e4ad
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3223_minimum_length_of_string_after_operations/SolutionTest.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3223_minimum_length_of_string_after_operations
+
+import org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo
+import org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
+
+internal class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ fun minimumLength() {
+ assertThat(Solution().minimumLength("abaacbcbb"), equalTo(5))
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun minimumLength2() {
+ assertThat(Solution().minimumLength("aa"), equalTo(2))
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3224_minimum_array_changes_to_make_differences_equal/SolutionTest.kt b/src/test/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3224_minimum_array_changes_to_make_differences_equal/SolutionTest.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..09932229c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3224_minimum_array_changes_to_make_differences_equal/SolutionTest.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3224_minimum_array_changes_to_make_differences_equal
+
+import org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo
+import org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
+
+internal class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ fun minChanges() {
+ assertThat(Solution().minChanges(intArrayOf(1, 0, 1, 2, 4, 3), 4), equalTo(2))
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun minChanges2() {
+ assertThat(Solution().minChanges(intArrayOf(0, 1, 2, 3, 3, 6, 5, 4), 6), equalTo(2))
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3225_maximum_score_from_grid_operations/SolutionTest.kt b/src/test/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3225_maximum_score_from_grid_operations/SolutionTest.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..f9801d2ef
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3225_maximum_score_from_grid_operations/SolutionTest.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,41 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3225_maximum_score_from_grid_operations
+
+import org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo
+import org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
+
+internal class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ fun maximumScore() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution()
+ .maximumScore(
+ arrayOf(
+ intArrayOf(0, 0, 0, 0, 0),
+ intArrayOf(0, 0, 3, 0, 0),
+ intArrayOf(0, 1, 0, 0, 0),
+ intArrayOf(5, 0, 0, 3, 0),
+ intArrayOf(0, 0, 0, 0, 2)
+ )
+ ),
+ equalTo(11L)
+ )
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun maximumScore2() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution()
+ .maximumScore(
+ arrayOf(
+ intArrayOf(10, 9, 0, 0, 15),
+ intArrayOf(7, 1, 0, 8, 0),
+ intArrayOf(5, 20, 0, 11, 0),
+ intArrayOf(0, 0, 0, 1, 2),
+ intArrayOf(8, 12, 1, 10, 3)
+ )
+ ),
+ equalTo(94L)
+ )
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3226_number_of_bit_changes_to_make_two_integers_equal/SolutionTest.kt b/src/test/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3226_number_of_bit_changes_to_make_two_integers_equal/SolutionTest.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..48521ec26
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3226_number_of_bit_changes_to_make_two_integers_equal/SolutionTest.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,22 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3226_number_of_bit_changes_to_make_two_integers_equal
+
+import org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo
+import org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
+
+internal class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ fun minChanges() {
+ assertThat(Solution().minChanges(13, 4), equalTo(2))
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun minChanges2() {
+ assertThat(Solution().minChanges(21, 21), equalTo(0))
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun minChanges3() {
+ assertThat(Solution().minChanges(14, 13), equalTo(-1))
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3227_vowels_game_in_a_string/SolutionTest.kt b/src/test/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3227_vowels_game_in_a_string/SolutionTest.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..fd9ca6fb3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3227_vowels_game_in_a_string/SolutionTest.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3227_vowels_game_in_a_string
+
+import org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo
+import org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
+
+internal class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ fun doesAliceWin() {
+ assertThat(Solution().doesAliceWin("leetcoder"), equalTo(true))
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun doesAliceWin2() {
+ assertThat(Solution().doesAliceWin("bbcd"), equalTo(false))
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3228_maximum_number_of_operations_to_move_ones_to_the_end/SolutionTest.kt b/src/test/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3228_maximum_number_of_operations_to_move_ones_to_the_end/SolutionTest.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..2abc29d67
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3228_maximum_number_of_operations_to_move_ones_to_the_end/SolutionTest.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3228_maximum_number_of_operations_to_move_ones_to_the_end
+
+import org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo
+import org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
+
+internal class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ fun maxOperations() {
+ assertThat(Solution().maxOperations("1001101"), equalTo(4))
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun maxOperations2() {
+ assertThat(Solution().maxOperations("00111"), equalTo(0))
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3229_minimum_operations_to_make_array_equal_to_target/SolutionTest.kt b/src/test/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3229_minimum_operations_to_make_array_equal_to_target/SolutionTest.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..588d7f4cf
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3229_minimum_operations_to_make_array_equal_to_target/SolutionTest.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3229_minimum_operations_to_make_array_equal_to_target
+
+import org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo
+import org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
+
+internal class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ fun minimumOperations() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution().minimumOperations(intArrayOf(3, 5, 1, 2), intArrayOf(4, 6, 2, 4)),
+ equalTo(2L)
+ )
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun minimumOperations2() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution().minimumOperations(intArrayOf(1, 3, 2), intArrayOf(2, 1, 4)),
+ equalTo(5L)
+ )
+ }
+}