diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3206_alternating_groups_i/Solution.kt b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3206_alternating_groups_i/Solution.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..3a0655b5d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3206_alternating_groups_i/Solution.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,22 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3206_alternating_groups_i
+
+// #Easy #Array #Sliding_Window #2024_07_11_Time_167_ms_(88.14%)_Space_38.3_MB_(23.73%)
+
+class Solution {
+ fun numberOfAlternatingGroups(colors: IntArray): Int {
+ val n = colors.size
+ var count = 0
+ if (colors[n - 1] != colors[0] && colors[0] != colors[1]) {
+ count++
+ }
+ if (colors[n - 1] != colors[0] && colors[n - 1] != colors[n - 2]) {
+ count++
+ }
+ for (i in 1 until n - 1) {
+ if (colors[i] != colors[i - 1] && colors[i] != colors[i + 1]) {
+ count++
+ }
+ }
+ return count
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3206_alternating_groups_i/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3206_alternating_groups_i/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..03dec61d4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3206_alternating_groups_i/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
+3206\. Alternating Groups I
+
+Easy
+
+There is a circle of red and blue tiles. You are given an array of integers `colors`. The color of tile `i` is represented by `colors[i]`:
+
+* `colors[i] == 0` means that tile `i` is **red**.
+* `colors[i] == 1` means that tile `i` is **blue**.
+
+Every 3 contiguous tiles in the circle with **alternating** colors (the middle tile has a different color from its **left** and **right** tiles) is called an **alternating** group.
+
+Return the number of **alternating** groups.
+
+**Note** that since `colors` represents a **circle**, the **first** and the **last** tiles are considered to be next to each other.
+
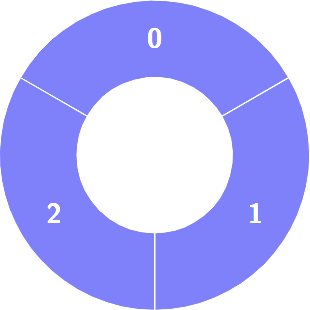
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** colors = [1,1,1]
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+
+
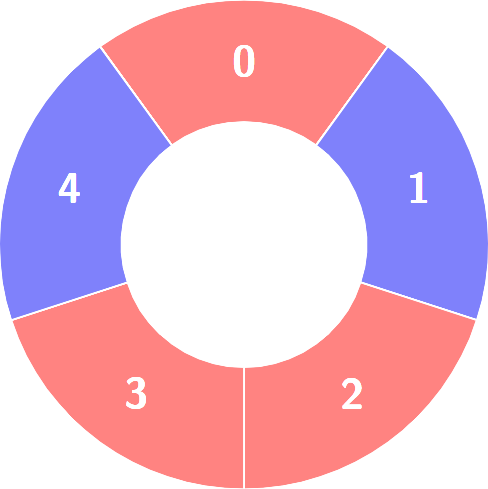
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** colors = [0,1,0,0,1]
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+
+
+Alternating groups:
+
+******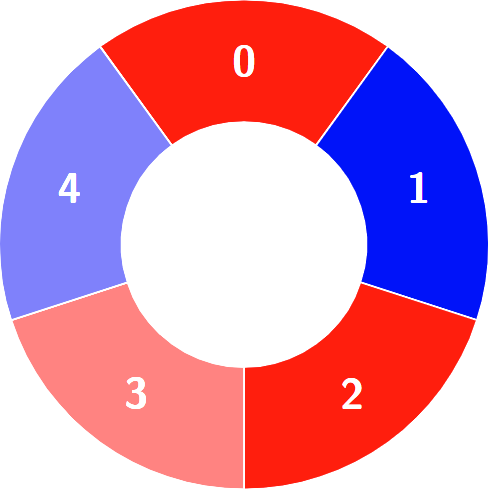**
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `3 <= colors.length <= 100`
+* `0 <= colors[i] <= 1`
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3207_maximum_points_after_enemy_battles/Solution.kt b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3207_maximum_points_after_enemy_battles/Solution.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..a25c924ea
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3207_maximum_points_after_enemy_battles/Solution.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,24 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3207_maximum_points_after_enemy_battles
+
+// #Medium #Array #Greedy #2024_07_11_Time_470_ms_(100.00%)_Space_62_MB_(95.56%)
+
+import kotlin.math.min
+
+class Solution {
+ fun maximumPoints(enemyEnergies: IntArray, currentEnergy: Int): Long {
+ val n = enemyEnergies.size
+ var min = enemyEnergies[0]
+ for (i in 1 until n) {
+ min = min(min.toDouble(), enemyEnergies[i].toDouble()).toInt()
+ }
+ if (currentEnergy == 0 || currentEnergy < min) {
+ return 0
+ }
+ var sum = currentEnergy.toLong()
+ for (i in n - 1 downTo 0) {
+ sum += enemyEnergies[i].toLong()
+ }
+ sum -= min.toLong()
+ return sum / min
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3207_maximum_points_after_enemy_battles/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3207_maximum_points_after_enemy_battles/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..694783a8a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3207_maximum_points_after_enemy_battles/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,52 @@
+3207\. Maximum Points After Enemy Battles
+
+Medium
+
+You are given an integer array `enemyEnergies` denoting the energy values of various enemies.
+
+You are also given an integer `currentEnergy` denoting the amount of energy you have initially.
+
+You start with 0 points, and all the enemies are unmarked initially.
+
+You can perform **either** of the following operations **zero** or multiple times to gain points:
+
+* Choose an **unmarked** enemy, `i`, such that `currentEnergy >= enemyEnergies[i]`. By choosing this option:
+ * You gain 1 point.
+ * Your energy is reduced by the enemy's energy, i.e. `currentEnergy = currentEnergy - enemyEnergies[i]`.
+* If you have **at least** 1 point, you can choose an **unmarked** enemy, `i`. By choosing this option:
+ * Your energy increases by the enemy's energy, i.e. `currentEnergy = currentEnergy + enemyEnergies[i]`.
+ * The enemy `i` is **marked**.
+
+Return an integer denoting the **maximum** points you can get in the end by optimally performing operations.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** enemyEnergies = [3,2,2], currentEnergy = 2
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+The following operations can be performed to get 3 points, which is the maximum:
+
+* First operation on enemy 1: `points` increases by 1, and `currentEnergy` decreases by 2. So, `points = 1`, and `currentEnergy = 0`.
+* Second operation on enemy 0: `currentEnergy` increases by 3, and enemy 0 is marked. So, `points = 1`, `currentEnergy = 3`, and marked enemies = `[0]`.
+* First operation on enemy 2: `points` increases by 1, and `currentEnergy` decreases by 2. So, `points = 2`, `currentEnergy = 1`, and marked enemies = `[0]`.
+* Second operation on enemy 2: `currentEnergy` increases by 2, and enemy 2 is marked. So, `points = 2`, `currentEnergy = 3`, and marked enemies = `[0, 2]`.
+* First operation on enemy 1: `points` increases by 1, and `currentEnergy` decreases by 2. So, `points = 3`, `currentEnergy = 1`, and marked enemies = `[0, 2]`.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** enemyEnergies = [2], currentEnergy = 10
+
+**Output:** 5
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+Performing the first operation 5 times on enemy 0 results in the maximum number of points.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= enemyEnergies.length <= 105
+* 1 <= enemyEnergies[i] <= 109
+* 0 <= currentEnergy <= 109
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3208_alternating_groups_ii/Solution.kt b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3208_alternating_groups_ii/Solution.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..e19767528
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3208_alternating_groups_ii/Solution.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3208_alternating_groups_ii
+
+// #Medium #Array #Sliding_Window #2024_07_11_Time_449_ms_(97.62%)_Space_59.6_MB_(100.00%)
+
+import kotlin.math.max
+
+class Solution {
+ fun numberOfAlternatingGroups(colors: IntArray, k: Int): Int {
+ var i = 0
+ var len = 0
+ var total = 0
+ while (i < colors.size - 1) {
+ var j = i + 1
+ if (colors[j] != colors[i]) {
+ len = 2
+ j++
+ while (j < colors.size && colors[j] != colors[j - 1]) {
+ j++
+ len++
+ }
+ if (j == colors.size) {
+ break
+ }
+ total += max(0, (len - k + 1))
+ }
+ i = j
+ len = 0
+ }
+ if (colors[0] != colors[colors.size - 1]) {
+ len = if (len == 0) 2 else len + 1
+ var j = 1
+ while (j < colors.size && colors[j] != colors[j - 1]) {
+ j++
+ len++
+ }
+ if (j >= k) {
+ len -= (j - k + 1)
+ }
+ }
+ total += max(0, (len - k + 1))
+ return total
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3208_alternating_groups_ii/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3208_alternating_groups_ii/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..73b6d5591
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3208_alternating_groups_ii/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,58 @@
+3208\. Alternating Groups II
+
+Medium
+
+There is a circle of red and blue tiles. You are given an array of integers `colors` and an integer `k`. The color of tile `i` is represented by `colors[i]`:
+
+* `colors[i] == 0` means that tile `i` is **red**.
+* `colors[i] == 1` means that tile `i` is **blue**.
+
+An **alternating** group is every `k` contiguous tiles in the circle with **alternating** colors (each tile in the group except the first and last one has a different color from its **left** and **right** tiles).
+
+Return the number of **alternating** groups.
+
+**Note** that since `colors` represents a **circle**, the **first** and the **last** tiles are considered to be next to each other.
+
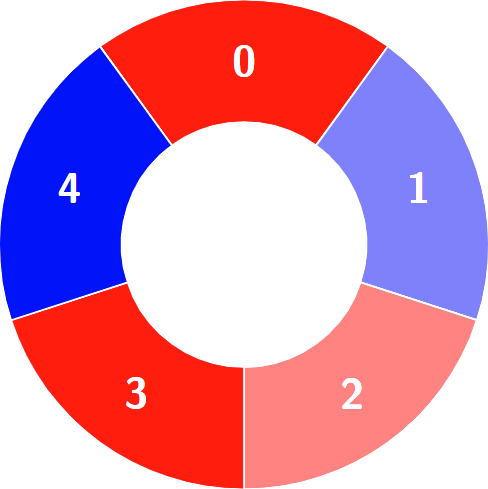
+**Example 1:**
+
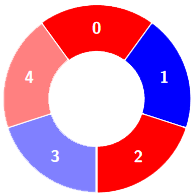
+**Input:** colors = [0,1,0,1,0], k = 3
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+**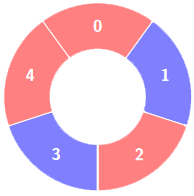**
+
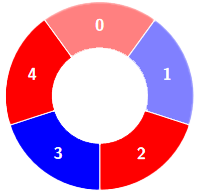
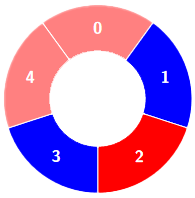
+Alternating groups:
+
+
+
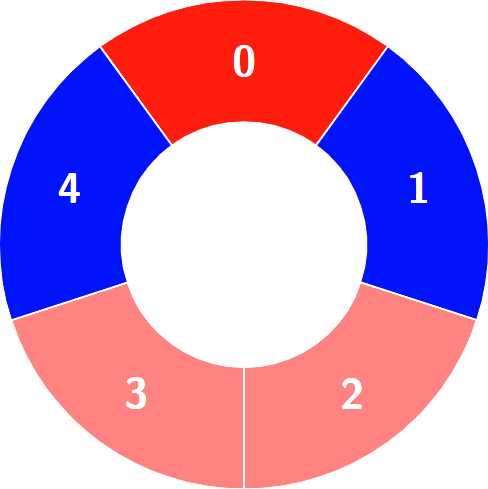
+**Example 2:**
+
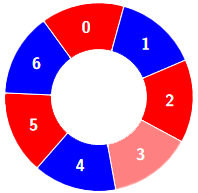
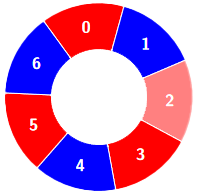
+**Input:** colors = [0,1,0,0,1,0,1], k = 6
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+**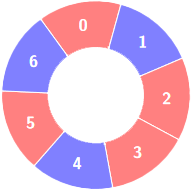**
+
+Alternating groups:
+
+
+
+**Example 3:**
+
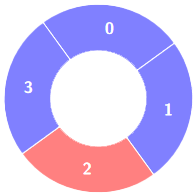
+**Input:** colors = [1,1,0,1], k = 4
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 3 <= colors.length <= 105
+* `0 <= colors[i] <= 1`
+* `3 <= k <= colors.length`
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3209_number_of_subarrays_with_and_value_of_k/Solution.kt b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3209_number_of_subarrays_with_and_value_of_k/Solution.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..03be1ec7b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3209_number_of_subarrays_with_and_value_of_k/Solution.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,28 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3209_number_of_subarrays_with_and_value_of_k
+
+// #Hard #Array #Binary_Search #Bit_Manipulation #Segment_Tree
+// #2024_07_11_Time_530_ms_(100.00%)_Space_58.2_MB_(76.19%)
+
+class Solution {
+ fun countSubarrays(nums: IntArray, k: Int): Long {
+ var ans: Long = 0
+ var left = 0
+ var right = 0
+ for (i in nums.indices) {
+ val x = nums[i]
+ var j = i - 1
+ while (j >= 0 && (nums[j] and x) != nums[j]) {
+ nums[j] = nums[j] and x
+ j--
+ }
+ while (left <= i && nums[left] < k) {
+ left++
+ }
+ while (right <= i && nums[right] <= k) {
+ right++
+ }
+ ans += (right - left).toLong()
+ }
+ return ans
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3209_number_of_subarrays_with_and_value_of_k/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3209_number_of_subarrays_with_and_value_of_k/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..3cf6d05f4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3209_number_of_subarrays_with_and_value_of_k/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,40 @@
+3209\. Number of Subarrays With AND Value of K
+
+Hard
+
+Given an array of integers `nums` and an integer `k`, return the number of subarrays of `nums` where the bitwise `AND` of the elements of the subarray equals `k`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,1,1], k = 1
+
+**Output:** 6
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+All subarrays contain only 1's.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,1,2], k = 1
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+Subarrays having an `AND` value of 1 are: [**1**,1,2], [1,**1**,2], [**1,1**,2].
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,2,3], k = 2
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+Subarrays having an `AND` value of 2 are: [1,**2**,3], [1,**2,3**].
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= nums.length <= 105
+* 0 <= nums[i], k <= 109
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3210_find_the_encrypted_string/Solution.kt b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3210_find_the_encrypted_string/Solution.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..37d6fcb34
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3210_find_the_encrypted_string/Solution.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,15 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3210_find_the_encrypted_string
+
+// #Easy #String #2024_07_11_Time_170_ms_(62.69%)_Space_35.5_MB_(67.16%)
+
+@Suppress("NAME_SHADOWING")
+class Solution {
+ fun getEncryptedString(s: String, k: Int): String {
+ var k = k
+ val n = s.length
+ k %= n
+ val str = StringBuilder(s.substring(k, n))
+ str.append(s.substring(0, k))
+ return str.toString()
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3210_find_the_encrypted_string/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3210_find_the_encrypted_string/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..08db6266f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3210_find_the_encrypted_string/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,38 @@
+3210\. Find the Encrypted String
+
+Easy
+
+You are given a string `s` and an integer `k`. Encrypt the string using the following algorithm:
+
+* For each character `c` in `s`, replace `c` with the kth character after `c` in the string (in a cyclic manner).
+
+Return the _encrypted string_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** s = "dart", k = 3
+
+**Output:** "tdar"
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+* For `i = 0`, the 3rd character after `'d'` is `'t'`.
+* For `i = 1`, the 3rd character after `'a'` is `'d'`.
+* For `i = 2`, the 3rd character after `'r'` is `'a'`.
+* For `i = 3`, the 3rd character after `'t'` is `'r'`.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** s = "aaa", k = 1
+
+**Output:** "aaa"
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+As all the characters are the same, the encrypted string will also be the same.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= s.length <= 100`
+* 1 <= k <= 104
+* `s` consists only of lowercase English letters.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3211_generate_binary_strings_without_adjacent_zeros/Solution.kt b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3211_generate_binary_strings_without_adjacent_zeros/Solution.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..0516c7080
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3211_generate_binary_strings_without_adjacent_zeros/Solution.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3211_generate_binary_strings_without_adjacent_zeros
+
+// #Medium #String #Bit_Manipulation #Recursion
+// #2024_07_11_Time_237_ms_(38.18%)_Space_45.3_MB_(5.45%)
+
+class Solution {
+ fun validStrings(n: Int): List {
+ val strings: MutableList = ArrayList()
+ dfs(n, StringBuilder(), strings)
+ return strings
+ }
+
+ private fun dfs(n: Int, build: StringBuilder, strings: MutableList) {
+ if (build.length == n) {
+ strings.add(build.toString())
+ return
+ }
+ // need to add a one
+ if (build.isNotEmpty() && build[build.length - 1] == '0') {
+ build.append('1')
+ dfs(n, build, strings)
+ // undo for backtracking
+ build.setLength(build.length - 1)
+ return
+ }
+ // choose to append a one
+ build.append('1')
+ dfs(n, build, strings)
+ build.setLength(build.length - 1)
+ // choose to append a zero
+ build.append('0')
+ dfs(n, build, strings)
+ build.setLength(build.length - 1)
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3211_generate_binary_strings_without_adjacent_zeros/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3211_generate_binary_strings_without_adjacent_zeros/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..87c61912f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3211_generate_binary_strings_without_adjacent_zeros/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
+3211\. Generate Binary Strings Without Adjacent Zeros
+
+Medium
+
+You are given a positive integer `n`.
+
+A binary string `x` is **valid** if all substrings of `x` of length 2 contain **at least** one `"1"`.
+
+Return all **valid** strings with length `n`**,** in _any_ order.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** n = 3
+
+**Output:** ["010","011","101","110","111"]
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+The valid strings of length 3 are: `"010"`, `"011"`, `"101"`, `"110"`, and `"111"`.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** n = 1
+
+**Output:** ["0","1"]
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+The valid strings of length 1 are: `"0"` and `"1"`.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= n <= 18`
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3212_count_submatrices_with_equal_frequency_of_x_and_y/Solution.kt b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3212_count_submatrices_with_equal_frequency_of_x_and_y/Solution.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..44c861ba4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3212_count_submatrices_with_equal_frequency_of_x_and_y/Solution.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,25 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3212_count_submatrices_with_equal_frequency_of_x_and_y
+
+// #Medium #Array #Matrix #Prefix_Sum #2024_07_11_Time_1009_ms_(78.95%)_Space_158.6_MB_(50.00%)
+
+class Solution {
+ fun numberOfSubmatrices(grid: Array): Int {
+ val n = grid[0].size
+ var ans = 0
+ val row = Array(n) { IntArray(2) }
+ for (chars in grid) {
+ val count = IntArray(2)
+ for (j in 0 until n) {
+ if (chars[j] != '.') {
+ count[chars[j].code - 'X'.code]++
+ }
+ row[j][0] += count[0]
+ row[j][1] += count[1]
+ if (row[j][0] > 0 && row[j][0] == row[j][1]) {
+ ans++
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return ans
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3212_count_submatrices_with_equal_frequency_of_x_and_y/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3212_count_submatrices_with_equal_frequency_of_x_and_y/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..5f0787647
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3212_count_submatrices_with_equal_frequency_of_x_and_y/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,44 @@
+3212\. Count Submatrices With Equal Frequency of X and Y
+
+Medium
+
+Given a 2D character matrix `grid`, where `grid[i][j]` is either `'X'`, `'Y'`, or `'.'`, return the number of submatrices that contains:
+
+* `grid[0][0]`
+* an **equal** frequency of `'X'` and `'Y'`.
+* **at least** one `'X'`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** grid = [["X","Y","."],["Y",".","."]]
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+**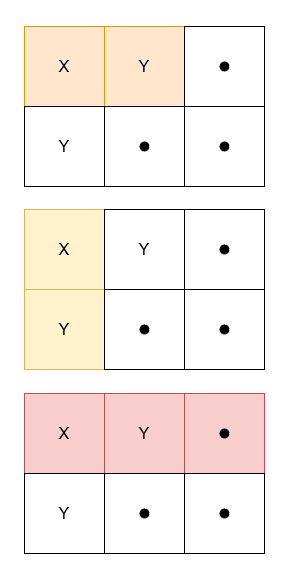**
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** grid = [["X","X"],["X","Y"]]
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+No submatrix has an equal frequency of `'X'` and `'Y'`.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** grid = [[".","."],[".","."]]
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+No submatrix has at least one `'X'`.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= grid.length, grid[i].length <= 1000`
+* `grid[i][j]` is either `'X'`, `'Y'`, or `'.'`.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3213_construct_string_with_minimum_cost/Solution.kt b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3213_construct_string_with_minimum_cost/Solution.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..727feeb8c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3213_construct_string_with_minimum_cost/Solution.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,66 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3213_construct_string_with_minimum_cost
+
+// #Hard #Array #String #Dynamic_Programming #Suffix_Array
+// #2024_07_09_Time_182_ms_(100.00%)_Space_61.4_MB_(72.97%)
+
+import kotlin.math.min
+
+class Solution {
+ private class Node {
+ var cost: Int = -1
+ var chd: Array = arrayOfNulls(26)
+ }
+
+ private var rt: Node? = null
+
+ fun minimumCost(target: String, words: Array, costs: IntArray): Int {
+ rt = Node()
+ val m = words.size
+ val n = target.length
+ for (i in 0 until m) {
+ if (words[i].length <= n) {
+ insert(words[i], costs[i])
+ }
+ }
+ val dp = IntArray(n + 1)
+ dp.fill(INVALID)
+ dp[0] = 0
+ for (i in 0 until n) {
+ if (dp[i] == INVALID) {
+ continue
+ }
+ val nowC = dp[i]
+ var now = rt
+ var j = i
+ while (now != null && j < n) {
+ val ch = target[j].code - 'a'.code
+ now = now.chd[ch]
+ if (now != null && now.cost != -1) {
+ dp[j + 1] = min(dp[j + 1].toDouble(), (nowC + now.cost).toDouble()).toInt()
+ }
+ ++j
+ }
+ }
+
+ return if (dp[n] == INVALID) -1 else dp[n]
+ }
+
+ private fun insert(wd: String, cst: Int) {
+ val len = wd.length
+ var now = rt
+ for (i in 0 until len) {
+ val ch = wd[i].code - 'a'.code
+ if (now!!.chd[ch] == null) {
+ now.chd[ch] = Node()
+ }
+ now = now.chd[ch]
+ }
+ if (now!!.cost == -1 || now.cost > cst) {
+ now.cost = cst
+ }
+ }
+
+ companion object {
+ private const val INVALID = Int.MAX_VALUE
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3213_construct_string_with_minimum_cost/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3213_construct_string_with_minimum_cost/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..a78d9bf21
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3213_construct_string_with_minimum_cost/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,48 @@
+3213\. Construct String with Minimum Cost
+
+Hard
+
+You are given a string `target`, an array of strings `words`, and an integer array `costs`, both arrays of the same length.
+
+Imagine an empty string `s`.
+
+You can perform the following operation any number of times (including **zero**):
+
+* Choose an index `i` in the range `[0, words.length - 1]`.
+* Append `words[i]` to `s`.
+* The cost of operation is `costs[i]`.
+
+Return the **minimum** cost to make `s` equal to `target`. If it's not possible, return `-1`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** target = "abcdef", words = ["abdef","abc","d","def","ef"], costs = [100,1,1,10,5]
+
+**Output:** 7
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+The minimum cost can be achieved by performing the following operations:
+
+* Select index 1 and append `"abc"` to `s` at a cost of 1, resulting in `s = "abc"`.
+* Select index 2 and append `"d"` to `s` at a cost of 1, resulting in `s = "abcd"`.
+* Select index 4 and append `"ef"` to `s` at a cost of 5, resulting in `s = "abcdef"`.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** target = "aaaa", words = ["z","zz","zzz"], costs = [1,10,100]
+
+**Output:** \-1
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+It is impossible to make `s` equal to `target`, so we return -1.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= target.length <= 5 * 104
+* 1 <= words.length == costs.length <= 5 * 104
+* `1 <= words[i].length <= target.length`
+* The total sum of `words[i].length` is less than or equal to 5 * 104.
+* `target` and `words[i]` consist only of lowercase English letters.
+* 1 <= costs[i] <= 104
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/test/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3206_alternating_groups_i/SolutionTest.kt b/src/test/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3206_alternating_groups_i/SolutionTest.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..051e0635d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3206_alternating_groups_i/SolutionTest.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,20 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3206_alternating_groups_i
+
+import org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo
+import org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
+
+internal class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ fun numberOfAlternatingGroups() {
+ assertThat(Solution().numberOfAlternatingGroups(intArrayOf(1, 1, 1)), equalTo(0))
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun numberOfAlternatingGroups2() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution().numberOfAlternatingGroups(intArrayOf(0, 1, 0, 0, 1)),
+ equalTo(3)
+ )
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3207_maximum_points_after_enemy_battles/SolutionTest.kt b/src/test/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3207_maximum_points_after_enemy_battles/SolutionTest.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..0b15eddb6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3207_maximum_points_after_enemy_battles/SolutionTest.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3207_maximum_points_after_enemy_battles
+
+import org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo
+import org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
+
+internal class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ fun maximumPoints() {
+ assertThat(Solution().maximumPoints(intArrayOf(3, 2, 2), 2), equalTo(3L))
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun maximumPoints2() {
+ assertThat(Solution().maximumPoints(intArrayOf(2), 10), equalTo(5L))
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3208_alternating_groups_ii/SolutionTest.kt b/src/test/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3208_alternating_groups_ii/SolutionTest.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..327671b1f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3208_alternating_groups_ii/SolutionTest.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,30 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3208_alternating_groups_ii
+
+import org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo
+import org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
+
+internal class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ fun numberOfAlternatingGroups() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution().numberOfAlternatingGroups(intArrayOf(0, 1, 0, 1, 0), 3), equalTo(3)
+ )
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun numberOfAlternatingGroups2() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution().numberOfAlternatingGroups(intArrayOf(0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1), 6),
+ equalTo(2)
+ )
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun numberOfAlternatingGroups3() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution().numberOfAlternatingGroups(intArrayOf(1, 1, 0, 1), 4),
+ equalTo(0)
+ )
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3209_number_of_subarrays_with_and_value_of_k/SolutionTest.kt b/src/test/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3209_number_of_subarrays_with_and_value_of_k/SolutionTest.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..f424cb542
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3209_number_of_subarrays_with_and_value_of_k/SolutionTest.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3209_number_of_subarrays_with_and_value_of_k
+
+import org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo
+import org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
+
+internal class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ fun countSubarrays() {
+ assertThat(Solution().countSubarrays(intArrayOf(1, 1, 2), 1), equalTo(3L))
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun countSubarrays2() {
+ assertThat(Solution().countSubarrays(intArrayOf(1, 2, 3), 2), equalTo(2L))
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3210_find_the_encrypted_string/SolutionTest.kt b/src/test/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3210_find_the_encrypted_string/SolutionTest.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..c0ccef3e8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3210_find_the_encrypted_string/SolutionTest.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3210_find_the_encrypted_string
+
+import org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo
+import org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
+
+internal class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ fun encryptedString() {
+ assertThat(Solution().getEncryptedString("dart", 3), equalTo("tdar"))
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun encryptedString2() {
+ assertThat(Solution().getEncryptedString("aaa", 1), equalTo("aaa"))
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3211_generate_binary_strings_without_adjacent_zeros/SolutionTest.kt b/src/test/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3211_generate_binary_strings_without_adjacent_zeros/SolutionTest.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..c9e3f6ded
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3211_generate_binary_strings_without_adjacent_zeros/SolutionTest.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,20 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3211_generate_binary_strings_without_adjacent_zeros
+
+import org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo
+import org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
+
+internal class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ fun validStrings() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution().validStrings(3),
+ equalTo(listOf("111", "110", "101", "011", "010"))
+ )
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun validStrings2() {
+ assertThat(Solution().validStrings(1), equalTo(listOf("1", "0")))
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3212_count_submatrices_with_equal_frequency_of_x_and_y/SolutionTest.kt b/src/test/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3212_count_submatrices_with_equal_frequency_of_x_and_y/SolutionTest.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..4f70810ac
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3212_count_submatrices_with_equal_frequency_of_x_and_y/SolutionTest.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3212_count_submatrices_with_equal_frequency_of_x_and_y
+
+import org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo
+import org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
+
+internal class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ fun numberOfSubmatrices() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution().numberOfSubmatrices(arrayOf(charArrayOf('X', 'Y', '.'), charArrayOf('Y', '.', '.'))),
+ equalTo(3)
+ )
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun numberOfSubmatrices2() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution().numberOfSubmatrices(arrayOf(charArrayOf('X', 'X'), charArrayOf('X', 'Y'))),
+ equalTo(0)
+ )
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun numberOfSubmatrices3() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution().numberOfSubmatrices(arrayOf(charArrayOf('.', '.'), charArrayOf('.', '.'))),
+ equalTo(0)
+ )
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3213_construct_string_with_minimum_cost/SolutionTest.kt b/src/test/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3213_construct_string_with_minimum_cost/SolutionTest.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..8118aa527
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3213_construct_string_with_minimum_cost/SolutionTest.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3213_construct_string_with_minimum_cost
+
+import org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo
+import org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
+
+internal class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ fun minimumCost() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution()
+ .minimumCost(
+ "abcdef",
+ arrayOf("abdef", "abc", "d", "def", "ef"),
+ intArrayOf(100, 1, 1, 10, 5)
+ ),
+ equalTo(7)
+ )
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun minimumCost2() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution()
+ .minimumCost(
+ "aaaa", arrayOf("z", "zz", "zzz"), intArrayOf(1, 10, 100)
+ ),
+ equalTo(-1)
+ )
+ }
+}