diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3200_maximum_height_of_a_triangle/Solution.kt b/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3200_maximum_height_of_a_triangle/Solution.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..5af8bb340
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3200_maximum_height_of_a_triangle/Solution.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,37 @@
+package g3101_3200.s3200_maximum_height_of_a_triangle
+
+// #Easy #Array #Enumeration #2024_07_06_Time_136_ms_(81.36%)_Space_33.8_MB_(28.81%)
+
+import kotlin.math.max
+
+@Suppress("NAME_SHADOWING")
+class Solution {
+ private fun count(v1: Int, v2: Int): Int {
+ var v1 = v1
+ var v2 = v2
+ var ct = 1
+ var flag = true
+ while (true) {
+ if (flag) {
+ if (ct <= v1) {
+ v1 -= ct
+ } else {
+ break
+ }
+ } else {
+ if (ct <= v2) {
+ v2 -= ct
+ } else {
+ break
+ }
+ }
+ ct++
+ flag = !flag
+ }
+ return ct - 1
+ }
+
+ fun maxHeightOfTriangle(red: Int, blue: Int): Int {
+ return max(count(red, blue), count(blue, red))
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3200_maximum_height_of_a_triangle/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3200_maximum_height_of_a_triangle/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..6f6de85a3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3200_maximum_height_of_a_triangle/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,53 @@
+3200\. Maximum Height of a Triangle
+
+Easy
+
+You are given two integers `red` and `blue` representing the count of red and blue colored balls. You have to arrange these balls to form a triangle such that the 1st row will have 1 ball, the 2nd row will have 2 balls, the 3rd row will have 3 balls, and so on.
+
+All the balls in a particular row should be the **same** color, and adjacent rows should have **different** colors.
+
+Return the **maximum** _height of the triangle_ that can be achieved.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** red = 2, blue = 4
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+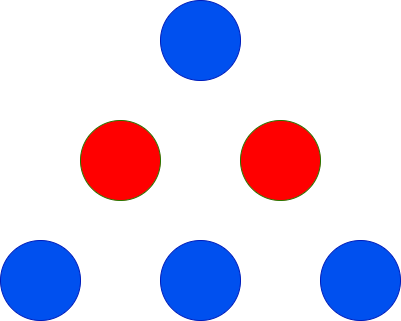
+
+The only possible arrangement is shown above.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** red = 2, blue = 1
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+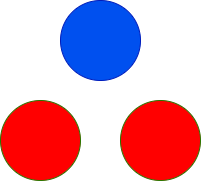
+ The only possible arrangement is shown above.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** red = 1, blue = 1
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Example 4:**
+
+**Input:** red = 10, blue = 1
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+
+ The only possible arrangement is shown above.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= red, blue <= 100`
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3201_find_the_maximum_length_of_valid_subsequence_i/Solution.kt b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3201_find_the_maximum_length_of_valid_subsequence_i/Solution.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..ad083da42
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3201_find_the_maximum_length_of_valid_subsequence_i/Solution.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,37 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3201_find_the_maximum_length_of_valid_subsequence_i
+
+// #Medium #Array #Dynamic_Programming #2024_07_06_Time_512_ms_(89.36%)_Space_62.1_MB_(76.60%)
+
+import kotlin.math.max
+
+class Solution {
+ fun maximumLength(nums: IntArray): Int {
+ val n = nums.size
+ var alter = 1
+ var odd = 0
+ var even = 0
+ if (nums[0] % 2 == 0) {
+ even++
+ } else {
+ odd++
+ }
+ var lastodd = nums[0] % 2 != 0
+ for (i in 1 until n) {
+ val flag = nums[i] % 2 == 0
+ if (flag) {
+ if (lastodd) {
+ alter++
+ lastodd = false
+ }
+ even++
+ } else {
+ if (!lastodd) {
+ alter++
+ lastodd = true
+ }
+ odd++
+ }
+ }
+ return max(alter, max(odd, even))
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3201_find_the_maximum_length_of_valid_subsequence_i/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3201_find_the_maximum_length_of_valid_subsequence_i/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..119c65799
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3201_find_the_maximum_length_of_valid_subsequence_i/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,48 @@
+3201\. Find the Maximum Length of Valid Subsequence I
+
+Medium
+
+You are given an integer array `nums`.
+
+A subsequence `sub` of `nums` with length `x` is called **valid** if it satisfies:
+
+* `(sub[0] + sub[1]) % 2 == (sub[1] + sub[2]) % 2 == ... == (sub[x - 2] + sub[x - 1]) % 2.`
+
+Return the length of the **longest** **valid** subsequence of `nums`.
+
+A **subsequence** is an array that can be derived from another array by deleting some or no elements without changing the order of the remaining elements.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,2,3,4]
+
+**Output:** 4
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+The longest valid subsequence is `[1, 2, 3, 4]`.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,2,1,1,2,1,2]
+
+**Output:** 6
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+The longest valid subsequence is `[1, 2, 1, 2, 1, 2]`.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,3]
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+The longest valid subsequence is `[1, 3]`.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 2 <= nums.length <= 2 * 105
+* 1 <= nums[i] <= 107
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3202_find_the_maximum_length_of_valid_subsequence_ii/Solution.kt b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3202_find_the_maximum_length_of_valid_subsequence_ii/Solution.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..0fe1affbd
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3202_find_the_maximum_length_of_valid_subsequence_ii/Solution.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,27 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3202_find_the_maximum_length_of_valid_subsequence_ii
+
+// #Medium #Array #Dynamic_Programming #2024_07_06_Time_255_ms_(97.30%)_Space_49_MB_(78.38%)
+
+import kotlin.math.max
+
+class Solution {
+ fun maximumLength(nums: IntArray, k: Int): Int {
+ // dp array to store the index against each possible modulo
+ val dp = Array(nums.size + 1) { IntArray(k + 1) }
+ var longest = 0
+ for (i in nums.indices) {
+ for (j in 0 until i) {
+ // Checking the modulo with each previous number
+ val `val` = (nums[i] + nums[j]) % k
+ // storing the number of pairs that have the same modulo.
+ // it would be one more than the number of pairs with the same modulo at the last
+ // index
+ dp[i][`val`] = dp[j][`val`] + 1
+ // Calculating the max seen till now
+ longest = max(longest, dp[i][`val`])
+ }
+ }
+ // total number of elements in the subsequence would be 1 more than the number of pairs
+ return longest + 1
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3202_find_the_maximum_length_of_valid_subsequence_ii/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3202_find_the_maximum_length_of_valid_subsequence_ii/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..5f79a06d4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3202_find_the_maximum_length_of_valid_subsequence_ii/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,37 @@
+3202\. Find the Maximum Length of Valid Subsequence II
+
+Medium
+
+You are given an integer array `nums` and a **positive** integer `k`.
+
+A subsequence `sub` of `nums` with length `x` is called **valid** if it satisfies:
+
+* `(sub[0] + sub[1]) % k == (sub[1] + sub[2]) % k == ... == (sub[x - 2] + sub[x - 1]) % k.`
+
+Return the length of the **longest** **valid** subsequence of `nums`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 2
+
+**Output:** 5
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+The longest valid subsequence is `[1, 2, 3, 4, 5]`.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,4,2,3,1,4], k = 3
+
+**Output:** 4
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+The longest valid subsequence is `[1, 4, 1, 4]`.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 2 <= nums.length <= 103
+* 1 <= nums[i] <= 107
+* 1 <= k <= 103
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3203_find_minimum_diameter_after_merging_two_trees/Solution.kt b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3203_find_minimum_diameter_after_merging_two_trees/Solution.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..445a08a34
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3203_find_minimum_diameter_after_merging_two_trees/Solution.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,86 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3203_find_minimum_diameter_after_merging_two_trees
+
+// #Hard #Depth_First_Search #Breadth_First_Search #Tree #Graph
+// #2024_07_06_Time_1156_ms_(100.00%)_Space_119.4_MB_(80.00%)
+
+import kotlin.math.max
+
+class Solution {
+ fun minimumDiameterAfterMerge(edges1: Array, edges2: Array): Int {
+ val n = edges1.size + 1
+ val g = packU(n, edges1)
+ val m = edges2.size + 1
+ val h = packU(m, edges2)
+ val d1 = diameter(g)
+ val d2 = diameter(h)
+ var ans = max(d1[0], d2[0])
+ ans = max(
+ ((d1[0] + 1) / 2 + ((d2[0] + 1) / 2) + 1),
+ ans
+ )
+ return ans
+ }
+
+ private fun diameter(g: Array): IntArray {
+ val n = g.size
+ val f0: Int
+ val f1: Int
+ val d01: Int
+ val q = IntArray(n)
+ val ved = BooleanArray(n)
+ var qp = 0
+ q[qp++] = 0
+ ved[0] = true
+ run {
+ var i = 0
+ while (i < qp) {
+ val cur = q[i]
+ for (e in g[cur]!!) {
+ if (!ved[e]) {
+ ved[e] = true
+ q[qp++] = e
+ }
+ }
+ i++
+ }
+ }
+ f0 = q[n - 1]
+ val d = IntArray(n)
+ qp = 0
+ ved.fill(false)
+ q[qp++] = f0
+ ved[f0] = true
+ var i = 0
+ while (i < qp) {
+ val cur = q[i]
+ for (e in g[cur]!!) {
+ if (!ved[e]) {
+ ved[e] = true
+ q[qp++] = e
+ d[e] = d[cur] + 1
+ }
+ }
+ i++
+ }
+ f1 = q[n - 1]
+ d01 = d[f1]
+ return intArrayOf(d01, f0, f1)
+ }
+
+ private fun packU(n: Int, ft: Array): Array {
+ val g = arrayOfNulls(n)
+ val p = IntArray(n)
+ for (u in ft) {
+ p[u[0]]++
+ p[u[1]]++
+ }
+ for (i in 0 until n) {
+ g[i] = IntArray(p[i])
+ }
+ for (u in ft) {
+ g[u[0]]!![--p[u[0]]] = u[1]
+ g[u[1]]!![--p[u[1]]] = u[0]
+ }
+ return g
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3203_find_minimum_diameter_after_merging_two_trees/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3203_find_minimum_diameter_after_merging_two_trees/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..27b313d83
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3203_find_minimum_diameter_after_merging_two_trees/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,45 @@
+3203\. Find Minimum Diameter After Merging Two Trees
+
+Hard
+
+There exist two **undirected** trees with `n` and `m` nodes, numbered from `0` to `n - 1` and from `0` to `m - 1`, respectively. You are given two 2D integer arrays `edges1` and `edges2` of lengths `n - 1` and `m - 1`, respectively, where edges1[i] = [ai, bi] indicates that there is an edge between nodes ai and bi in the first tree and edges2[i] = [ui, vi] indicates that there is an edge between nodes ui and vi in the second tree.
+
+You must connect one node from the first tree with another node from the second tree with an edge.
+
+Return the **minimum** possible **diameter** of the resulting tree.
+
+The **diameter** of a tree is the length of the _longest_ path between any two nodes in the tree.
+
+**Example 1:**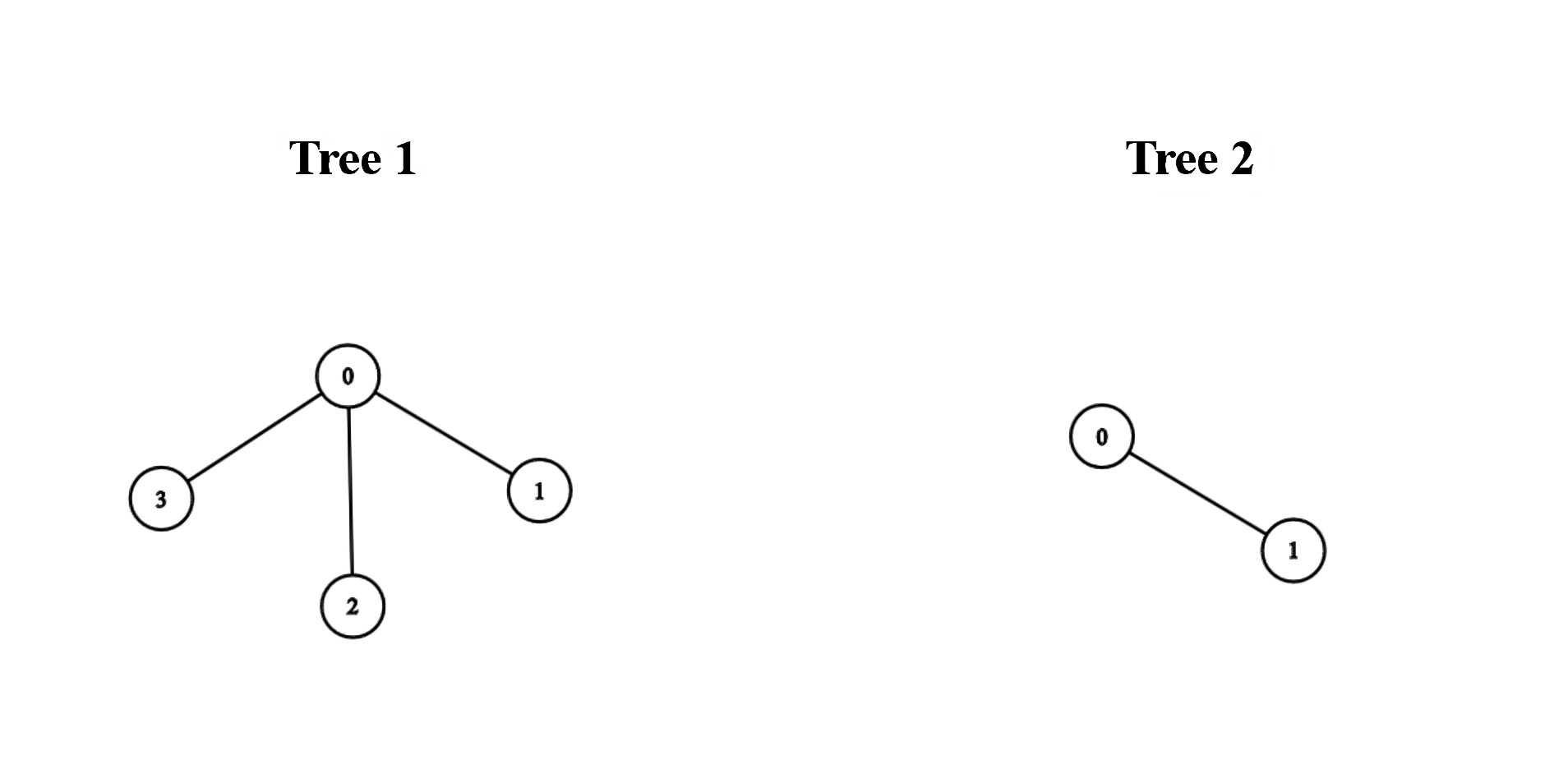
+
+**Input:** edges1 = [[0,1],[0,2],[0,3]], edges2 = [[0,1]]
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+We can obtain a tree of diameter 3 by connecting node 0 from the first tree with any node from the second tree.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+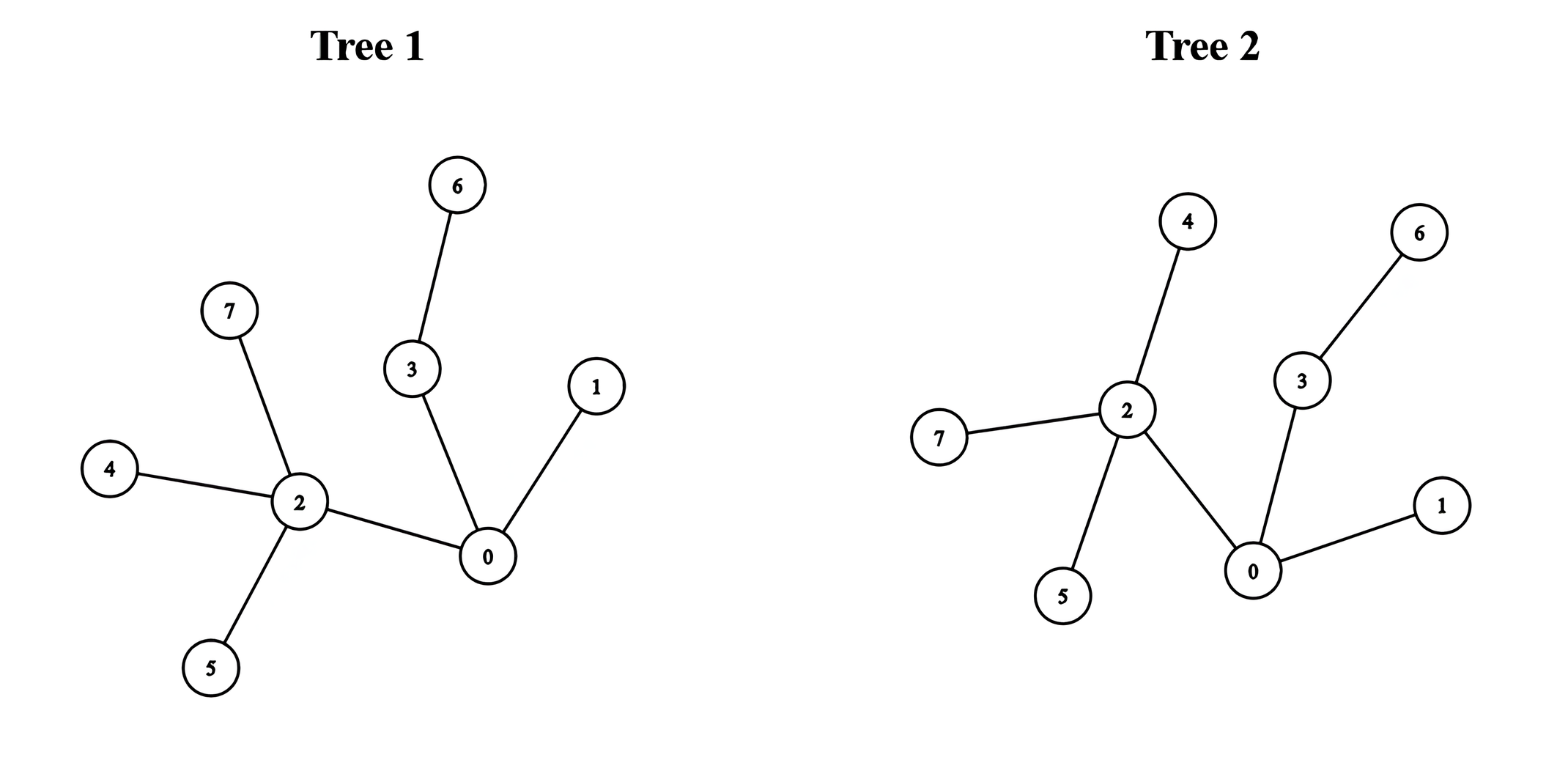
+
+**Input:** edges1 = [[0,1],[0,2],[0,3],[2,4],[2,5],[3,6],[2,7]], edges2 = [[0,1],[0,2],[0,3],[2,4],[2,5],[3,6],[2,7]]
+
+**Output:** 5
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+We can obtain a tree of diameter 5 by connecting node 0 from the first tree with node 0 from the second tree.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= n, m <= 105
+* `edges1.length == n - 1`
+* `edges2.length == m - 1`
+* `edges1[i].length == edges2[i].length == 2`
+* edges1[i] = [ai, bi]
+* 0 <= ai, bi < n
+* edges2[i] = [ui, vi]
+* 0 <= ui, vi < m
+* The input is generated such that `edges1` and `edges2` represent valid trees.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/test/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3200_maximum_height_of_a_triangle/SolutionTest.kt b/src/test/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3200_maximum_height_of_a_triangle/SolutionTest.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..281467794
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3200_maximum_height_of_a_triangle/SolutionTest.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
+package g3101_3200.s3200_maximum_height_of_a_triangle
+
+import org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo
+import org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
+
+internal class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ fun maxHeightOfTriangle() {
+ assertThat(Solution().maxHeightOfTriangle(2, 4), equalTo(3))
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun maxHeightOfTriangle2() {
+ assertThat(Solution().maxHeightOfTriangle(2, 1), equalTo(2))
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3201_find_the_maximum_length_of_valid_subsequence_i/SolutionTest.kt b/src/test/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3201_find_the_maximum_length_of_valid_subsequence_i/SolutionTest.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..ea855e12d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3201_find_the_maximum_length_of_valid_subsequence_i/SolutionTest.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3201_find_the_maximum_length_of_valid_subsequence_i
+
+import org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo
+import org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
+
+internal class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ fun maximumLength() {
+ assertThat(Solution().maximumLength(intArrayOf(1, 2, 3, 4)), equalTo(4))
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun maximumLength2() {
+ assertThat(Solution().maximumLength(intArrayOf(1, 2, 1, 1, 2, 1, 2)), equalTo(6))
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3202_find_the_maximum_length_of_valid_subsequence_ii/SolutionTest.kt b/src/test/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3202_find_the_maximum_length_of_valid_subsequence_ii/SolutionTest.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..81d8c1dd3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3202_find_the_maximum_length_of_valid_subsequence_ii/SolutionTest.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3202_find_the_maximum_length_of_valid_subsequence_ii
+
+import org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo
+import org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
+
+internal class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ fun maximumLength() {
+ assertThat(Solution().maximumLength(intArrayOf(1, 2, 3, 4, 5), 2), equalTo(5))
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun maximumLength2() {
+ assertThat(Solution().maximumLength(intArrayOf(1, 4, 2, 3, 1, 4), 3), equalTo(4))
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3203_find_minimum_diameter_after_merging_two_trees/SolutionTest.kt b/src/test/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3203_find_minimum_diameter_after_merging_two_trees/SolutionTest.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..509563fe2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3203_find_minimum_diameter_after_merging_two_trees/SolutionTest.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,46 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3203_find_minimum_diameter_after_merging_two_trees
+
+import org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo
+import org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
+
+internal class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ fun minimumDiameterAfterMerge() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution()
+ .minimumDiameterAfterMerge(
+ arrayOf(intArrayOf(0, 1), intArrayOf(0, 2), intArrayOf(0, 3)), arrayOf(intArrayOf(0, 1))
+ ),
+ equalTo(3)
+ )
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun minimumDiameterAfterMerge2() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution()
+ .minimumDiameterAfterMerge(
+ arrayOf(
+ intArrayOf(0, 1),
+ intArrayOf(0, 2),
+ intArrayOf(0, 3),
+ intArrayOf(2, 4),
+ intArrayOf(2, 5),
+ intArrayOf(3, 6),
+ intArrayOf(2, 7)
+ ),
+ arrayOf(
+ intArrayOf(0, 1),
+ intArrayOf(0, 2),
+ intArrayOf(0, 3),
+ intArrayOf(2, 4),
+ intArrayOf(2, 5),
+ intArrayOf(3, 6),
+ intArrayOf(2, 7)
+ )
+ ),
+ equalTo(5)
+ )
+ }
+}