diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3190_find_minimum_operations_to_make_all_elements_divisible_by_three/Solution.kt b/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3190_find_minimum_operations_to_make_all_elements_divisible_by_three/Solution.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..12f75020f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3190_find_minimum_operations_to_make_all_elements_divisible_by_three/Solution.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,15 @@
+package g3101_3200.s3190_find_minimum_operations_to_make_all_elements_divisible_by_three
+
+// #Easy #Array #Math #2024_06_29_Time_153_ms_(87.95%)_Space_34.7_MB_(74.70%)
+
+class Solution {
+ fun minimumOperations(nums: IntArray): Int {
+ var count = 0
+ for (i in nums.indices) {
+ if (nums[i] % 3 != 0) {
+ count++
+ }
+ }
+ return count
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3190_find_minimum_operations_to_make_all_elements_divisible_by_three/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3190_find_minimum_operations_to_make_all_elements_divisible_by_three/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..e91729d4e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3190_find_minimum_operations_to_make_all_elements_divisible_by_three/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,32 @@
+3190\. Find Minimum Operations to Make All Elements Divisible by Three
+
+Easy
+
+You are given an integer array `nums`. In one operation, you can add or subtract 1 from **any** element of `nums`.
+
+Return the **minimum** number of operations to make all elements of `nums` divisible by 3.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,2,3,4]
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+All array elements can be made divisible by 3 using 3 operations:
+
+* Subtract 1 from 1.
+* Add 1 to 2.
+* Subtract 1 from 4.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [3,6,9]
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= nums.length <= 50`
+* `1 <= nums[i] <= 50`
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3191_minimum_operations_to_make_binary_array_elements_equal_to_one_i/Solution.kt b/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3191_minimum_operations_to_make_binary_array_elements_equal_to_one_i/Solution.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..058321b1f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3191_minimum_operations_to_make_binary_array_elements_equal_to_one_i/Solution.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,28 @@
+package g3101_3200.s3191_minimum_operations_to_make_binary_array_elements_equal_to_one_i
+
+// #Medium #Array #Bit_Manipulation #Prefix_Sum #Sliding_Window #Queue
+// #2024_06_29_Time_653_ms_(57.35%)_Space_73.6_MB_(30.88%)
+
+class Solution {
+ fun minOperations(nums: IntArray): Int {
+ var ans = 0
+ // Iterate through the array up to the third-last element
+ for (i in 0 until nums.size - 2) {
+ // If the current element is 0, perform an operation
+ if (nums[i] == 0) {
+ ans++
+ // Flip the current element and the next two elements
+ nums[i] = 1
+ nums[i + 1] = if (nums[i + 1] == 0) 1 else 0
+ nums[i + 2] = if (nums[i + 2] == 0) 1 else 0
+ }
+ }
+ // Check the last two elements if they are 0, return -1 as they cannot be flipped
+ for (i in nums.size - 2 until nums.size) {
+ if (nums[i] == 0) {
+ return -1
+ }
+ }
+ return ans
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3191_minimum_operations_to_make_binary_array_elements_equal_to_one_i/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3191_minimum_operations_to_make_binary_array_elements_equal_to_one_i/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..fcd72690c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3191_minimum_operations_to_make_binary_array_elements_equal_to_one_i/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,40 @@
+3191\. Minimum Operations to Make Binary Array Elements Equal to One I
+
+Medium
+
+You are given a binary array `nums`.
+
+You can do the following operation on the array **any** number of times (possibly zero):
+
+* Choose **any** 3 **consecutive** elements from the array and **flip** **all** of them.
+
+**Flipping** an element means changing its value from 0 to 1, and from 1 to 0.
+
+Return the **minimum** number of operations required to make all elements in `nums` equal to 1. If it is impossible, return -1.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [0,1,1,1,0,0]
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:**
+ We can do the following operations:
+
+* Choose the elements at indices 0, 1 and 2. The resulting array is nums = [**1**,**0**,**0**,1,0,0].
+* Choose the elements at indices 1, 2 and 3. The resulting array is nums = [1,**1**,**1**,**0**,0,0].
+* Choose the elements at indices 3, 4 and 5. The resulting array is nums = [1,1,1,**1**,**1**,**1**].
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [0,1,1,1]
+
+**Output:** \-1
+
+**Explanation:**
+ It is impossible to make all elements equal to 1.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 3 <= nums.length <= 105
+* `0 <= nums[i] <= 1`
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3192_minimum_operations_to_make_binary_array_elements_equal_to_one_ii/Solution.kt b/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3192_minimum_operations_to_make_binary_array_elements_equal_to_one_ii/Solution.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..c58d60636
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3192_minimum_operations_to_make_binary_array_elements_equal_to_one_ii/Solution.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,18 @@
+package g3101_3200.s3192_minimum_operations_to_make_binary_array_elements_equal_to_one_ii
+
+// #Medium #Array #Dynamic_Programming #Greedy
+// #2024_06_29_Time_684_ms_(64.29%)_Space_70.9_MB_(62.50%)
+
+class Solution {
+ fun minOperations(nums: IntArray): Int {
+ var a = 0
+ var c = 1
+ for (x in nums) {
+ if (x != c) {
+ a++
+ c = c xor 1
+ }
+ }
+ return a
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3192_minimum_operations_to_make_binary_array_elements_equal_to_one_ii/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3192_minimum_operations_to_make_binary_array_elements_equal_to_one_ii/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..be9ddd643
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3192_minimum_operations_to_make_binary_array_elements_equal_to_one_ii/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
+3192\. Minimum Operations to Make Binary Array Elements Equal to One II
+
+Medium
+
+You are given a binary array `nums`.
+
+You can do the following operation on the array **any** number of times (possibly zero):
+
+* Choose **any** index `i` from the array and **flip** **all** the elements from index `i` to the end of the array.
+
+**Flipping** an element means changing its value from 0 to 1, and from 1 to 0.
+
+Return the **minimum** number of operations required to make all elements in `nums` equal to 1.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [0,1,1,0,1]
+
+**Output:** 4
+
+**Explanation:**
+ We can do the following operations:
+
+* Choose the index `i = 1`. The resulting array will be nums = [0,**0**,**0**,**1**,**0**].
+* Choose the index `i = 0`. The resulting array will be nums = [**1**,**1**,**1**,**0**,**1**].
+* Choose the index `i = 4`. The resulting array will be nums = [1,1,1,0,**0**].
+* Choose the index `i = 3`. The resulting array will be nums = [1,1,1,**1**,**1**].
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,0,0,0]
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Explanation:**
+ We can do the following operation:
+
+* Choose the index `i = 1`. The resulting array will be nums = [1,**1**,**1**,**1**].
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= nums.length <= 105
+* `0 <= nums[i] <= 1`
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3193_count_the_number_of_inversions/Solution.kt b/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3193_count_the_number_of_inversions/Solution.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..456436949
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3193_count_the_number_of_inversions/Solution.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,47 @@
+package g3101_3200.s3193_count_the_number_of_inversions
+
+// #Hard #Array #Dynamic_Programming #2024_06_29_Time_243_ms_(94.74%)_Space_45.5_MB_(100.00%)
+
+class Solution {
+ fun numberOfPermutations(n: Int, r: Array): Int {
+ r.sortWith { o1: IntArray, o2: IntArray -> o1[0] - o2[0] }
+ if (r[0][0] == 0 && r[0][1] > 0) {
+ return 0
+ }
+ var ri = if (r[0][0] == 0) 1 else 0
+ var a: Long = 1
+ var t: Long
+ val m = Array(n) { IntArray(401) }
+ m[0][0] = 1
+ for (i in 1 until m.size) {
+ m[i][0] = m[i - 1][0]
+ for (j in 1..i) {
+ m[i][j] = (m[i][j] + m[i][j - 1]) % MOD
+ m[i][j] = (m[i][j] + m[i - 1][j]) % MOD
+ }
+ for (j in i + 1..r[ri][1]) {
+ m[i][j] = (m[i][j] + m[i][j - 1]) % MOD
+ m[i][j] = (m[i][j] + m[i - 1][j]) % MOD
+ m[i][j] = (m[i][j] - m[i - 1][j - i - 1])
+ if (m[i][j] < 0) {
+ m[i][j] += MOD
+ }
+ }
+ if (r[ri][0] == i) {
+ t = m[i][r[ri][1]].toLong()
+ if (t == 0L) {
+ return 0
+ }
+ m[i].fill(0)
+ m[i][r[ri][1]] = 1
+ a = (a * t) % MOD
+ ri++
+ }
+ }
+ return a.toInt()
+ }
+
+ companion object {
+ private const val MOD = 1000000007
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3193_count_the_number_of_inversions/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3193_count_the_number_of_inversions/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..0ca16695a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3193_count_the_number_of_inversions/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,67 @@
+3193\. Count the Number of Inversions
+
+Hard
+
+You are given an integer `n` and a 2D array `requirements`, where requirements[i] = [endi, cnti] represents the end index and the **inversion** count of each requirement.
+
+A pair of indices `(i, j)` from an integer array `nums` is called an **inversion** if:
+
+* `i < j` and `nums[i] > nums[j]`
+
+Return the number of permutations `perm` of `[0, 1, 2, ..., n - 1]` such that for **all** `requirements[i]`, perm[0..endi] has exactly cnti inversions.
+
+Since the answer may be very large, return it **modulo** 109 + 7.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** n = 3, requirements = [[2,2],[0,0]]
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+The two permutations are:
+
+* `[2, 0, 1]`
+ * Prefix `[2, 0, 1]` has inversions `(0, 1)` and `(0, 2)`.
+ * Prefix `[2]` has 0 inversions.
+* `[1, 2, 0]`
+ * Prefix `[1, 2, 0]` has inversions `(0, 2)` and `(1, 2)`.
+ * Prefix `[1]` has 0 inversions.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** n = 3, requirements = [[2,2],[1,1],[0,0]]
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+The only satisfying permutation is `[2, 0, 1]`:
+
+* Prefix `[2, 0, 1]` has inversions `(0, 1)` and `(0, 2)`.
+* Prefix `[2, 0]` has an inversion `(0, 1)`.
+* Prefix `[2]` has 0 inversions.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** n = 2, requirements = [[0,0],[1,0]]
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+The only satisfying permutation is `[0, 1]`:
+
+* Prefix `[0]` has 0 inversions.
+* Prefix `[0, 1]` has an inversion `(0, 1)`.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `2 <= n <= 300`
+* `1 <= requirements.length <= n`
+* requirements[i] = [endi, cnti]
+* 0 <= endi <= n - 1
+* 0 <= cnti <= 400
+* The input is generated such that there is at least one `i` such that endi == n - 1.
+* The input is generated such that all endi are unique.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3194_minimum_average_of_smallest_and_largest_elements/Solution.kt b/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3194_minimum_average_of_smallest_and_largest_elements/Solution.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..0049eda51
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3194_minimum_average_of_smallest_and_largest_elements/Solution.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,19 @@
+package g3101_3200.s3194_minimum_average_of_smallest_and_largest_elements
+
+// #Easy #Array #Sorting #Two_Pointers #2024_06_29_Time_192_ms_(94.25%)_Space_41_MB_(49.43%)
+
+import kotlin.math.min
+
+class Solution {
+ fun minimumAverage(nums: IntArray): Double {
+ nums.sort()
+ var m = 102.0
+ var i = 0
+ val l = nums.size
+ while (i < l / 2) {
+ m = min(m, nums[i] + nums[l - i - 1].toDouble())
+ i++
+ }
+ return m / 2.0
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3194_minimum_average_of_smallest_and_largest_elements/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3194_minimum_average_of_smallest_and_largest_elements/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..4c1801f3d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3194_minimum_average_of_smallest_and_largest_elements/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,66 @@
+3194\. Minimum Average of Smallest and Largest Elements
+
+Easy
+
+You have an array of floating point numbers `averages` which is initially empty. You are given an array `nums` of `n` integers where `n` is even.
+
+You repeat the following procedure `n / 2` times:
+
+* Remove the **smallest** element, `minElement`, and the **largest** element `maxElement`, from `nums`.
+* Add `(minElement + maxElement) / 2` to `averages`.
+
+Return the **minimum** element in `averages`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [7,8,3,4,15,13,4,1]
+
+**Output:** 5.5
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+| Step | nums | averages |
+|------|------------------|------------|
+| 0 | [7,8,3,4,15,13,4,1] | [] |
+| 1 | [7,8,3,4,13,4] | [8] |
+| 2 | [7,8,4,4] | [8, 8] |
+| 3 | [7,4] | [8, 8, 6] |
+| 4 | [] | [8, 8, 6, 5.5] |
+
+The smallest element of averages, 5.5, is returned.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,9,8,3,10,5]
+
+**Output:** 5.5
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+| Step | nums | averages |
+|------|----------------|------------|
+| 0 | [1,9,8,3,10,5] | [] |
+| 1 | [9,8,3,5] | [5.5] |
+| 2 | [8,5] | [5.5, 6] |
+| 3 | [] | [5.5, 6, 6.5] |
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,2,3,7,8,9]
+
+**Output:** 5.0
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+| Step | nums | averages |
+|------|----------------|------------|
+| 0 | [1,2,3,7,8,9] | [] |
+| 1 | [2,3,7,8] | [5] |
+| 2 | [3,7] | [5, 5] |
+| 3 | [] | [5, 5, 5] |
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `2 <= n == nums.length <= 50`
+* `n` is even.
+* `1 <= nums[i] <= 50`
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3195_find_the_minimum_area_to_cover_all_ones_i/Solution.kt b/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3195_find_the_minimum_area_to_cover_all_ones_i/Solution.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..83ff538d1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3195_find_the_minimum_area_to_cover_all_ones_i/Solution.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,30 @@
+package g3101_3200.s3195_find_the_minimum_area_to_cover_all_ones_i
+
+// #Medium #Array #Matrix #2024_06_29_Time_1068_ms_(73.91%)_Space_212.6_MB_(47.83%)
+
+import kotlin.math.max
+import kotlin.math.min
+
+class Solution {
+ fun minimumArea(grid: Array): Int {
+ var xmin = Int.MAX_VALUE
+ var xmax = -1
+ var ymin = Int.MAX_VALUE
+ var ymax = -1
+ var i = 0
+ val m = grid.size
+ val n = grid[0].size
+ while (i < m) {
+ for (j in 0 until n) {
+ if (grid[i][j] == 1) {
+ xmin = min(xmin, i)
+ xmax = max(xmax, i)
+ ymin = min(ymin, j)
+ ymax = max(ymax, j)
+ }
+ }
+ i++
+ }
+ return (xmax - xmin + 1) * (ymax - ymin + 1)
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3195_find_the_minimum_area_to_cover_all_ones_i/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3195_find_the_minimum_area_to_cover_all_ones_i/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..2467b25a0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3195_find_the_minimum_area_to_cover_all_ones_i/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,37 @@
+3195\. Find the Minimum Area to Cover All Ones I
+
+Medium
+
+You are given a 2D **binary** array `grid`. Find a rectangle with horizontal and vertical sides with the **smallest** area, such that all the 1's in `grid` lie inside this rectangle.
+
+Return the **minimum** possible area of the rectangle.
+
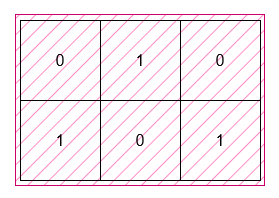
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** grid = [[0,1,0],[1,0,1]]
+
+**Output:** 6
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+
+
+The smallest rectangle has a height of 2 and a width of 3, so it has an area of `2 * 3 = 6`.
+
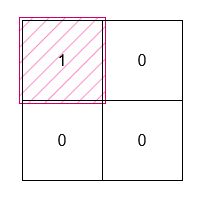
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** grid = [[1,0],[0,0]]
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+
+
+The smallest rectangle has both height and width 1, so its area is `1 * 1 = 1`.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= grid.length, grid[i].length <= 1000`
+* `grid[i][j]` is either 0 or 1.
+* The input is generated such that there is at least one 1 in `grid`.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3196_maximize_total_cost_of_alternating_subarrays/Solution.kt b/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3196_maximize_total_cost_of_alternating_subarrays/Solution.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..24e11fee2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3196_maximize_total_cost_of_alternating_subarrays/Solution.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,20 @@
+package g3101_3200.s3196_maximize_total_cost_of_alternating_subarrays
+
+// #Medium #Array #Dynamic_Programming #2024_06_29_Time_496_ms_(73.81%)_Space_64.2_MB_(80.95%)
+
+import kotlin.math.max
+
+class Solution {
+ fun maximumTotalCost(nums: IntArray): Long {
+ val n = nums.size
+ var addResult = nums[0].toLong()
+ var subResult = nums[0].toLong()
+ for (i in 1 until n) {
+ val tempAdd = (max(addResult.toDouble(), subResult.toDouble()) + nums[i]).toLong()
+ val tempSub = addResult - nums[i]
+ addResult = tempAdd
+ subResult = tempSub
+ }
+ return max(addResult, subResult)
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3196_maximize_total_cost_of_alternating_subarrays/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3196_maximize_total_cost_of_alternating_subarrays/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..03cb06af3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3196_maximize_total_cost_of_alternating_subarrays/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,64 @@
+3196\. Maximize Total Cost of Alternating Subarrays
+
+Medium
+
+You are given an integer array `nums` with length `n`.
+
+The **cost** of a subarray `nums[l..r]`, where `0 <= l <= r < n`, is defined as:
+
+cost(l, r) = nums[l] - nums[l + 1] + ... + nums[r] * (−1)r − l
+
+Your task is to **split** `nums` into subarrays such that the **total** **cost** of the subarrays is **maximized**, ensuring each element belongs to **exactly one** subarray.
+
+Formally, if `nums` is split into `k` subarrays, where `k > 1`, at indices i1, i2, ..., ik − 1, where 0 <= i1 < i2 < ... < ik - 1 < n - 1, then the total cost will be:
+
+cost(0, i1) + cost(i1 + 1, i2) + ... + cost(ik − 1 + 1, n − 1)
+
+Return an integer denoting the _maximum total cost_ of the subarrays after splitting the array optimally.
+
+**Note:** If `nums` is not split into subarrays, i.e. `k = 1`, the total cost is simply `cost(0, n - 1)`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,-2,3,4]
+
+**Output:** 10
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+One way to maximize the total cost is by splitting `[1, -2, 3, 4]` into subarrays `[1, -2, 3]` and `[4]`. The total cost will be `(1 + 2 + 3) + 4 = 10`.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,-1,1,-1]
+
+**Output:** 4
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+One way to maximize the total cost is by splitting `[1, -1, 1, -1]` into subarrays `[1, -1]` and `[1, -1]`. The total cost will be `(1 + 1) + (1 + 1) = 4`.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [0]
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+We cannot split the array further, so the answer is 0.
+
+**Example 4:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,-1]
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+Selecting the whole array gives a total cost of `1 + 1 = 2`, which is the maximum.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= nums.length <= 105
+* -109 <= nums[i] <= 109
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3197_find_the_minimum_area_to_cover_all_ones_ii/Solution.kt b/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3197_find_the_minimum_area_to_cover_all_ones_ii/Solution.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..615eb8284
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3197_find_the_minimum_area_to_cover_all_ones_ii/Solution.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,144 @@
+package g3101_3200.s3197_find_the_minimum_area_to_cover_all_ones_ii
+
+// #Hard #Array #Matrix #Enumeration #2024_06_29_Time_216_ms_(100.00%)_Space_40.1_MB_(80.00%)
+
+import kotlin.math.min
+
+class Solution {
+ // rectangle unit count
+ private lateinit var ruc: Array
+ private var height = 0
+ private var width = 0
+
+ // r0, c0 incl., r1, c1 excl.
+ private fun unitsInRectangle(r0: Int, c0: Int, r1: Int, c1: Int): Int {
+ return ruc[r1][c1] - ruc[r0][c1] - ruc[r1][c0] + ruc[r0][c0]
+ }
+
+ private fun minArea(r0: Int, c0: Int, r1: Int, c1: Int): Int {
+ if (unitsInRectangle(r0, c0, r1, c1) == 0) {
+ return 0
+ }
+ var minRow = r0
+ while (unitsInRectangle(r0, c0, minRow + 1, c1) == 0) {
+ minRow++
+ }
+ var maxRow = r1 - 1
+ while (unitsInRectangle(maxRow, c0, r1, c1) == 0) {
+ maxRow--
+ }
+ var minCol = c0
+ while (unitsInRectangle(r0, c0, r1, minCol + 1) == 0) {
+ minCol++
+ }
+ var maxCol = c1 - 1
+ while (unitsInRectangle(r0, maxCol, r1, c1) == 0) {
+ maxCol--
+ }
+ return (maxRow - minRow + 1) * (maxCol - minCol + 1)
+ }
+
+ private fun minSum2(r0: Int, c0: Int, r1: Int, c1: Int, splitVertical: Boolean): Int {
+ var min = Int.MAX_VALUE
+ if (splitVertical) {
+ for (c in c0 + 1 until c1) {
+ val a1 = minArea(r0, c0, r1, c)
+ if (a1 == 0) {
+ continue
+ }
+ val a2 = minArea(r0, c, r1, c1)
+ if (a2 != 0) {
+ min = min(min, (a1 + a2))
+ }
+ }
+ } else {
+ for (r in r0 + 1 until r1) {
+ val a1 = minArea(r0, c0, r, c1)
+ if (a1 == 0) {
+ continue
+ }
+ val a2 = minArea(r, c0, r1, c1)
+ if (a2 != 0) {
+ min = min(min, (a1 + a2))
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return min
+ }
+
+ private fun minSum3(
+ firstSplitVertical: Boolean,
+ takeLower: Boolean,
+ secondSplitVertical: Boolean
+ ): Int {
+ var min = Int.MAX_VALUE
+ if (firstSplitVertical) {
+ for (c in 1 until width) {
+ var a1: Int
+ var a2: Int
+ if (takeLower) {
+ a1 = minArea(0, 0, height, c)
+ if (a1 == 0) {
+ continue
+ }
+ a2 = minSum2(0, c, height, width, secondSplitVertical)
+ } else {
+ a1 = minArea(0, c, height, width)
+ if (a1 == 0) {
+ continue
+ }
+ a2 = minSum2(0, 0, height, c, secondSplitVertical)
+ }
+ if (a2 != Int.MAX_VALUE) {
+ min = min(min, (a1 + a2))
+ }
+ }
+ } else {
+ for (r in 1 until height) {
+ var a1: Int
+ var a2: Int
+ if (takeLower) {
+ a1 = minArea(0, 0, r, width)
+ if (a1 == 0) {
+ continue
+ }
+ a2 = minSum2(r, 0, height, width, secondSplitVertical)
+ } else {
+ a1 = minArea(r, 0, height, width)
+ if (a1 == 0) {
+ continue
+ }
+ a2 = minSum2(0, 0, r, width, secondSplitVertical)
+ }
+ if (a2 != Int.MAX_VALUE) {
+ min = min(min, (a1 + a2))
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return min
+ }
+
+ fun minimumSum(grid: Array): Int {
+ height = grid.size
+ width = grid[0].size
+ ruc = Array(height + 1) { IntArray(width + 1) }
+ for (i in 0 until height) {
+ val gRow = grid[i]
+ val cRow0 = ruc[i]
+ val cRow1 = ruc[i + 1]
+ var c = 0
+ for (j in 0 until width) {
+ c += gRow[j]
+ cRow1[j + 1] = cRow0[j + 1] + c
+ }
+ }
+ var min = Int.MAX_VALUE
+ min = min(min, minSum3(true, true, true))
+ min = min(min, minSum3(true, true, false))
+ min = min(min, minSum3(true, false, false))
+ min = min(min, minSum3(false, true, true))
+ min = min(min, minSum3(false, true, false))
+ min = min(min, minSum3(false, false, true))
+ return min
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3197_find_the_minimum_area_to_cover_all_ones_ii/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3197_find_the_minimum_area_to_cover_all_ones_ii/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..e1d35dbbb
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3197_find_the_minimum_area_to_cover_all_ones_ii/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
+3197\. Find the Minimum Area to Cover All Ones II
+
+Hard
+
+You are given a 2D **binary** array `grid`. You need to find 3 **non-overlapping** rectangles having **non-zero** areas with horizontal and vertical sides such that all the 1's in `grid` lie inside these rectangles.
+
+Return the **minimum** possible sum of the area of these rectangles.
+
+**Note** that the rectangles are allowed to touch.
+
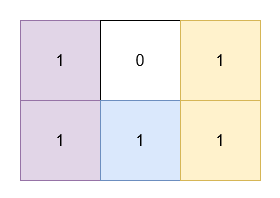
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** grid = [[1,0,1],[1,1,1]]
+
+**Output:** 5
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+
+
+* The 1's at `(0, 0)` and `(1, 0)` are covered by a rectangle of area 2.
+* The 1's at `(0, 2)` and `(1, 2)` are covered by a rectangle of area 2.
+* The 1 at `(1, 1)` is covered by a rectangle of area 1.
+
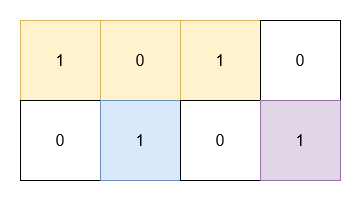
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** grid = [[1,0,1,0],[0,1,0,1]]
+
+**Output:** 5
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+
+
+* The 1's at `(0, 0)` and `(0, 2)` are covered by a rectangle of area 3.
+* The 1 at `(1, 1)` is covered by a rectangle of area 1.
+* The 1 at `(1, 3)` is covered by a rectangle of area 1.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= grid.length, grid[i].length <= 30`
+* `grid[i][j]` is either 0 or 1.
+* The input is generated such that there are at least three 1's in `grid`.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/test/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3190_find_minimum_operations_to_make_all_elements_divisible_by_three/SolutionTest.kt b/src/test/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3190_find_minimum_operations_to_make_all_elements_divisible_by_three/SolutionTest.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..c345514fe
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3190_find_minimum_operations_to_make_all_elements_divisible_by_three/SolutionTest.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
+package g3101_3200.s3190_find_minimum_operations_to_make_all_elements_divisible_by_three
+
+import org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo
+import org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
+
+internal class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ fun minimumOperations() {
+ assertThat(Solution().minimumOperations(intArrayOf(1, 2, 3, 4)), equalTo(3))
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun minimumOperations2() {
+ assertThat(Solution().minimumOperations(intArrayOf(3, 6, 9)), equalTo(0))
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3191_minimum_operations_to_make_binary_array_elements_equal_to_one_i/SolutionTest.kt b/src/test/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3191_minimum_operations_to_make_binary_array_elements_equal_to_one_i/SolutionTest.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..6129b4f8e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3191_minimum_operations_to_make_binary_array_elements_equal_to_one_i/SolutionTest.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
+package g3101_3200.s3191_minimum_operations_to_make_binary_array_elements_equal_to_one_i
+
+import org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo
+import org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
+
+internal class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ fun minOperations() {
+ assertThat(Solution().minOperations(intArrayOf(0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0)), equalTo(3))
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun minOperations2() {
+ assertThat(Solution().minOperations(intArrayOf(0, 1, 1, 1)), equalTo(-1))
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3192_minimum_operations_to_make_binary_array_elements_equal_to_one_ii/SolutionTest.kt b/src/test/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3192_minimum_operations_to_make_binary_array_elements_equal_to_one_ii/SolutionTest.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..d2c12835a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3192_minimum_operations_to_make_binary_array_elements_equal_to_one_ii/SolutionTest.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
+package g3101_3200.s3192_minimum_operations_to_make_binary_array_elements_equal_to_one_ii
+
+import org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo
+import org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
+
+internal class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ fun minOperations() {
+ assertThat(Solution().minOperations(intArrayOf(0, 1, 1, 0, 1)), equalTo(4))
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun minOperations2() {
+ assertThat(Solution().minOperations(intArrayOf(1, 0, 0, 0)), equalTo(1))
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3193_count_the_number_of_inversions/SolutionTest.kt b/src/test/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3193_count_the_number_of_inversions/SolutionTest.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..889f0c150
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3193_count_the_number_of_inversions/SolutionTest.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,29 @@
+package g3101_3200.s3193_count_the_number_of_inversions
+
+import org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo
+import org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
+
+internal class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ fun numberOfPermutations() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution().numberOfPermutations(3, arrayOf(intArrayOf(2, 2), intArrayOf(0, 0))), equalTo(2)
+ )
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun numberOfPermutations2() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution().numberOfPermutations(3, arrayOf(intArrayOf(2, 2), intArrayOf(1, 1), intArrayOf(0, 0))),
+ equalTo(1)
+ )
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun numberOfPermutations3() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution().numberOfPermutations(2, arrayOf(intArrayOf(0, 0), intArrayOf(1, 0))), equalTo(1)
+ )
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3194_minimum_average_of_smallest_and_largest_elements/SolutionTest.kt b/src/test/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3194_minimum_average_of_smallest_and_largest_elements/SolutionTest.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..a711e97c1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3194_minimum_average_of_smallest_and_largest_elements/SolutionTest.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,24 @@
+package g3101_3200.s3194_minimum_average_of_smallest_and_largest_elements
+
+import org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo
+import org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
+
+internal class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ fun minimumAverage() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution().minimumAverage(intArrayOf(7, 8, 3, 4, 15, 13, 4, 1)), equalTo(5.5)
+ )
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun minimumAverage2() {
+ assertThat(Solution().minimumAverage(intArrayOf(1, 9, 8, 3, 10, 5)), equalTo(5.5))
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun minimumAverage3() {
+ assertThat(Solution().minimumAverage(intArrayOf(1, 2, 3, 7, 8, 9)), equalTo(5.0))
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3195_find_the_minimum_area_to_cover_all_ones_i/SolutionTest.kt b/src/test/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3195_find_the_minimum_area_to_cover_all_ones_i/SolutionTest.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..3480937b4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3195_find_the_minimum_area_to_cover_all_ones_i/SolutionTest.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
+package g3101_3200.s3195_find_the_minimum_area_to_cover_all_ones_i
+
+import org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo
+import org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
+
+internal class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ fun minimumArea() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution().minimumArea(arrayOf(intArrayOf(0, 1, 0), intArrayOf(1, 0, 1))),
+ equalTo(6)
+ )
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun minimumArea2() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution().minimumArea(arrayOf(intArrayOf(1, 0), intArrayOf(0, 0))),
+ equalTo(1)
+ )
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3196_maximize_total_cost_of_alternating_subarrays/SolutionTest.kt b/src/test/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3196_maximize_total_cost_of_alternating_subarrays/SolutionTest.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..4fe058529
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3196_maximize_total_cost_of_alternating_subarrays/SolutionTest.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,27 @@
+package g3101_3200.s3196_maximize_total_cost_of_alternating_subarrays
+
+import org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo
+import org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
+
+internal class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ fun maximumTotalCost() {
+ assertThat(Solution().maximumTotalCost(intArrayOf(1, -2, 3, 4)), equalTo(10L))
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun maximumTotalCost2() {
+ assertThat(Solution().maximumTotalCost(intArrayOf(1, -1, 1, -1)), equalTo(4L))
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun maximumTotalCost3() {
+ assertThat(Solution().maximumTotalCost(intArrayOf(0)), equalTo(0L))
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun maximumTotalCost4() {
+ assertThat(Solution().maximumTotalCost(intArrayOf(1, -1)), equalTo(2L))
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3197_find_the_minimum_area_to_cover_all_ones_ii/SolutionTest.kt b/src/test/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3197_find_the_minimum_area_to_cover_all_ones_ii/SolutionTest.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..e0bf08693
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3197_find_the_minimum_area_to_cover_all_ones_ii/SolutionTest.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
+package g3101_3200.s3197_find_the_minimum_area_to_cover_all_ones_ii
+
+import org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo
+import org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
+
+internal class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ fun minimumSum() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution().minimumSum(arrayOf(intArrayOf(1, 0, 1), intArrayOf(1, 1, 1))),
+ equalTo(5)
+ )
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun minimumSum2() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution().minimumSum(arrayOf(intArrayOf(1, 0, 1, 0), intArrayOf(0, 1, 0, 1))),
+ equalTo(5)
+ )
+ }
+}